Expression and Localization of an Hsp70 Protein in the Microsporidian Encephalitozoon cuniculi
- PMID: 20811483
- PMCID: PMC2926585
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/523654
Expression and Localization of an Hsp70 Protein in the Microsporidian Encephalitozoon cuniculi
Abstract
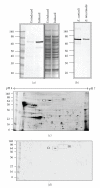
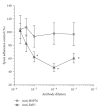
Microsporidia spore surface proteins are an important, under investigated aspect of spore/host cell attachment and infection. For comparison analysis of surface proteins, we required an antibody control specific for an intracellular protein. An endoplasmic reticulum-associated heat shock protein 70 family member (Hsp70; ECU02_0100; "C1") was chosen for further analysis. DNA encoding the C1 hsp70 was amplified, cloned and used to heterologously express the C1 Hsp70 protein, and specific antiserum was generated. Two-dimensional Western blotting analysis showed that the purified antibodies were monospecific. Immunoelectron microscopy of developing and mature E. cuniculi spores revealed that the protein localized to internal structures and not to the spore surface. In spore adherence inhibition assays, the anti-C1 antibodies did not inhibit spore adherence to host cell surfaces, whereas antibodies to a known surface adhesin (EnP1) did so. In future studies, the antibodies to the 'C1' Hsp70 will be used to delineate spore surface protein expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
EnP1, a microsporidian spore wall protein that enables spores to adhere to and infect host cells in vitro.Eukaryot Cell. 2007 Aug;6(8):1354-62. doi: 10.1128/EC.00113-07. Epub 2007 Jun 8. Eukaryot Cell. 2007. PMID: 17557882 Free PMC article.
-
EnP1 and EnP2, two proteins associated with the Encephalitozoon cuniculi endospore, the chitin-rich inner layer of the microsporidian spore wall.Int J Parasitol. 2006 Mar;36(3):309-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.10.005. Epub 2005 Nov 22. Int J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16368098
-
Characterization of Hsp70 gene family provides insight into its functions related to microsporidian proliferation.J Invertebr Pathol. 2020 Jul;174:107394. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2020.107394. Epub 2020 May 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32428446
-
Spore-forming microsporidian encephalitozoon: current understanding of infection and prevention in Japan.Jpn J Infect Dis. 2009 Nov;62(6):413-22. Jpn J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19934531 Review.
-
Microsporidia: emerging pathogenic protists.Acta Trop. 2001 Feb 23;78(2):89-102. doi: 10.1016/s0001-706x(00)00178-9. Acta Trop. 2001. PMID: 11230819 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of mass spectrometry to elucidate the pathophysiology of Encephalitozoon cuniculi infection in rabbits.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 19;12(7):e0177961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177961. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28723944 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desportes-Livage I. Microsporidia and other opportunistic protozoa in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) 1996;1(Clinical Microbiology and Infection):152–153. - PubMed
-
- Kotler DP, Orenstein JM. Clinical syndromes associated with microsporidiosis. Advances in Parasitology. 1998;40:321–349. - PubMed
-
- Hartl FU, Martin J, Neupert W. Protein folding in the cell: the role of molecular chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp60. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure. 1992;21:293–322. - PubMed
-
- Hayman JR, Nash TE. Isolating expressed microsporidial genes using a cDNA subtractive hybridization approach. Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology. 1999;46(5):21S–24S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

