Herpes simplex virus type 1/adeno-associated virus hybrid vectors
- PMID: 20811580
- PMCID: PMC2930156
- DOI: 10.2174/1874357901004030109
Herpes simplex virus type 1/adeno-associated virus hybrid vectors
Abstract
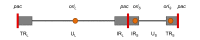
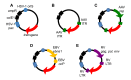
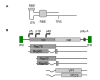
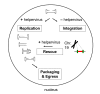
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) amplicons can accommodate foreign DNA of any size up to 150 kbp and, therefore, allow extensive combinations of genetic elements. Genomic sequences as well as cDNA, large transcriptional regulatory sequences for cell type-specific expression, multiple transgenes, and genetic elements from other viruses to create hybrid vectors may be inserted in a modular fashion. Hybrid amplicons use genetic elements from HSV-1 that allow replication and packaging of the vector DNA into HSV-1 virions, and genetic elements from other viruses that either direct integration of transgene sequences into the host genome or allow episomal maintenance of the vector. Thus, the advantages of the HSV-1 amplicon system, including large transgene capacity, broad host range, strong nuclear localization, and availability of helper virus-free packaging systems are retained and combined with those of heterologous viral elements that confer genetic stability to the vector DNA. Adeno-associated virus (AAV) has the unique capability of integrating its genome into a specific site, designated AAVS1, on human chromosome 19. The AAV rep gene and the inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) that flank the AAV genome are sufficient for this process. HSV-1 amplicons have thus been designed that contain the rep gene and a transgene cassette flanked by AAV ITRs. These HSV/AAV hybrid vectors direct site-specific integration of transgene sequences into AAVS1 and support long-term transgene expression.
Keywords: HSV-1 amplicon vectors; adeno-associated virus; herpes simplex virus type 1; hybrid vectors..
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and packaging of herpes simplex virus/adeno-associated virus (HSV/AAV) Hybrid amplicon vectors.Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2012 Mar 1;2012(3):352-6. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot068114. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2012. PMID: 22383640
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1/adeno-associated virus hybrid vectors mediate site-specific integration at the adeno-associated virus preintegration site, AAVS1, on human chromosome 19.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):7163-73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7163-7173.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072516 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1/adeno-associated virus rep(+) hybrid amplicon vector improves the stability of transgene expression in human cells by site-specific integration.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(14):7150-62. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.14.7150-7162.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12072515 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric herpes simplex virus/adeno-associated virus amplicon vectors.Curr Gene Ther. 2006 Jun;6(3):315-24. doi: 10.2174/156652306777592090. Curr Gene Ther. 2006. PMID: 16787183 Review.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 amplicons and their hybrid virus partners, EBV, AAV, and retrovirus.Curr Gene Ther. 2004 Dec;4(4):385-408. doi: 10.2174/1566523043346129. Curr Gene Ther. 2004. PMID: 15578989 Review.
Cited by
-
High-brightness anterograde transneuronal HSV1 H129 tracer modified using a Trojan horse-like strategy.Mol Brain. 2020 Jan 13;13(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-0544-2. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 31931837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davison MD, Rixon FJ, Davison AJ. Identification of genes encoding two capsid proteins (VP24 and VP26) of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1992;73(pt 10):2709–13. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson JG, Yang K, Baines JD, Homa FL. Linker insertion mutations in the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL28 gene: effects on UL28 interaction with UL15 and UL33 and identification of a second-site mutation in the UL15 gene that suppresses a lethal UL28 mutation. J Virol. 2006;80:12312–23. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
