Aging and immune function: molecular mechanisms to interventions
- PMID: 20812785
- PMCID: PMC3061194
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2010.3228
Aging and immune function: molecular mechanisms to interventions
Abstract
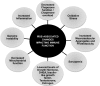
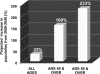
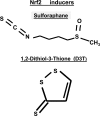
Abstract The immune system of an organism is an essential component of the defense mechanism aimed at combating pathogenic stress. Age-associated immune dysfunction, also dubbed "immune senescence," manifests as increased susceptibility to infections, increased onset and progression of autoimmune diseases, and onset of neoplasia. Over the years, extensive research has generated consensus in terms of the phenotypic and functional defects within the immune system in various organisms, including humans. Indeed, age-associated alterations such as thymic involution, T cell repertoire skewing, decreased ability to activate naïve T cells and to generate robust memory responses, have been shown to have a causative role in immune decline. Further, understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the generation of proteotoxic stress, DNA damage response, modulation of ubiquitin proteasome pathway, and regulation of transcription factor NFκB activation, in immune decline, have paved the way to delineating signaling pathways that cross-talk and impact immune senescence. Given the role of the immune system in combating infections, its effectiveness with age may well be a marker of health and a predictor of longevity. It is therefore believed that a better understanding of the mechanisms underlying immune senescence will lead to an effective interventional strategy aimed at improving the health span of individuals. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 14, 1551-1585.
Figures








Similar articles
-
The aging immune system: primer and prospectus.Science. 1996 Jul 5;273(5271):70-4. doi: 10.1126/science.273.5271.70. Science. 1996. PMID: 8658199 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of aging and immune system regulation in Drosophila.Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(8):9826-9844. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089826. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22949833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell generation dynamics underlying naive T-cell homeostasis in adult humans.PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 29;17(10):e3000383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000383. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31661488 Free PMC article.
-
Aging of the Immune System. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Dec;13 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S422-S428. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201602-095AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 28005419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cells and aging, January 2002 update.Front Biosci. 2002 May 1;7:d1056-183. doi: 10.2741/a831. Front Biosci. 2002. PMID: 11991846 Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuins, aging, and cardiovascular risks.Age (Dordr). 2015 Aug;37(4):9804. doi: 10.1007/s11357-015-9804-y. Epub 2015 Jun 23. Age (Dordr). 2015. PMID: 26099749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating Predictors of Decannulation Through Endoscopic Approach in Patients With Tracheostomy and Peristomal Subglottic Stenosis.OTO Open. 2024 Oct 16;8(4):e70033. doi: 10.1002/oto2.70033. eCollection 2024 Oct-Dec. OTO Open. 2024. PMID: 39421398 Free PMC article.
-
How can Biology of Aging Explain the Severity of COVID-19 in Older Adults.Clin Geriatr Med. 2022 Aug;38(3):461-472. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2022.04.002. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Clin Geriatr Med. 2022. PMID: 35868666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on Old and Weary Haematopoiesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 29;19(9):2567. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092567. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30158459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impairment of immunoproteasome function by β5i/LMP7 subunit deficiency results in severe enterovirus myocarditis.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Sep;7(9):e1002233. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002233. Epub 2011 Sep 1. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21909276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adolfsson O. Huber BT. Meydani SN. Vitamin E-enhanced IL-2 production in old mice: naive but not memory T cells show increased cell division cycling and IL-2-producing capacity. J Immunol. 2001;167:3809–3817. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A. Agrawal S. Cao JN. Su H. Osann K. Gupta S. Altered innate immune functioning of dendritic cells in elderly humans: a role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2007;178:6912–6922. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama M. Yamada O. Hideshima T. Yanagisawa T. Yokoi K. Fujisawa K. Eto Y. Yamada H. Anderson KC. TNFalpha induces rapid activation and nuclear translocation of telomerase in human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316:528–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

