Hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration reduce intradialytic hypotension in ESRD
- PMID: 20813866
- PMCID: PMC3013537
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010030280
Hemofiltration and hemodiafiltration reduce intradialytic hypotension in ESRD
Abstract
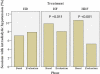
Symptomatic intradialytic hypotension is a common complication of hemodialysis (HD). The application of convective therapies to the outpatient setting may improve outcomes, including intradialytic hypotension. In this multicenter, open-label, randomized controlled study, we randomly assigned 146 long-term dialysis patients to HD (n = 70), online predilution hemofiltration (HF; n = 36), or online predilution hemodiafiltration (HDF; n = 40). The primary end point was the frequency of intradialytic symptomatic hypotension (ISH). Compared with the run-in period, the frequency of sessions with ISH during the evaluation period increased for HD (7.1 to 7.9%) and decreased for both HF (9.8 to 8.0%) and HDF (10.6 to 5.2%) (P < 0.001). Mean predialysis systolic BP increased by 4.2 mmHg among those who were assigned to HDF compared with decreases of 0.6 and 1.8 mmHg among those who were assigned to HD and HF, respectively (P = 0.038). Multivariate logistic regression demonstrated significant risk reductions in ISH for both HF (odds ratio 0.69; 95% confidence interval 0.51 to 0.92) and HDF (odds ratio 0.46, 95% confidence interval 0.33 to 0.63). There was a trend toward higher dropout for those who were assigned to HF (P = 0.107). In conclusion, compared with conventional HD, convective therapies (HDF and HF) reduce ISH in long-term dialysis patients.
Figures

Comment in
-
Convective therapies reduce risk of intradialytic hypotension.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010 Dec;6(12):691. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2010.146. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 21155066 No abstract available.
References
-
- Andrulli S, Colzani S, Mascia F, Lucchi L, Stipo L, Bigi MC, Crepaldi M, Redaelli B, Albertazzi A, Locatelli F: The role of blood volume reduction in the genesis of intradialytic hypotension. Am J Kidney Dis 40: 1244–1254, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Tislér A, Akócsi K, Borbás B, Fazakas L, Ferenczi S, Görögh S, Kulcsár I, Nagy L, Sámik J, Szegedi J, Tóth E, Wágner G, Kiss I: The effect of frequent or occasional dialysis-associated hypotension on survival of patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18: 2601–2605, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Altieri P, Sorba GB, Bolasco PG, Bostrom M, Asproni E, Ferrara R, Bolasco F, Cossu M, Cadinu F, Cabiddu GF, Casu D, Ganadu M, Passaghe P, Pinna M: On line predilution hemofiltration versus ultrapure high-flux hemodialysis: A multicenter prospective study in 23 patients. Blood Purif 15: 169–181, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Altieri P, Sorba GB, Bolasco PG, Asproni E, Ledevo I, Cossu M, Ferrara R, Ganadu M, Cadinu M, Serra G, Cabiddu G, Sau G, Casu D, Passaghe M, Bolasco F, Pistis R, Ghisu T: Predilution haemofiltration: The Second Sardinian Multicentre Study—Comparison between haemofiltration and haemodialysis during identical Kt/V and session times in a long-term cross-over study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16: 1207–1213, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Hornberger JC, Chernew M, Petersen J, Garber AM: A multivariate analysis of mortality and hospital admissions with high flux dialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 3: 1227–1237, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

