Ductal aneurysm masquerading as nonresolving pneumonia: A challenging differential!
- PMID: 20814482
- PMCID: PMC2921525
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-2069.64364
Ductal aneurysm masquerading as nonresolving pneumonia: A challenging differential!
Abstract
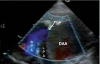
We report here, the case of a six-and-a-half-month-old boy investigated for persistent respiratory distress and homogeneous opacity in the left upper lobe. Echocardiography revealed a giant ductal aneurysm compressing the left pulmonary artery and upper lobe division of the left bronchus. Computerized tomography angiogram delineated the exact anatomy and prompt surgical resection provided a successful cure to this lesser known entity.
Keywords: Ductal aneurysm; PDA; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



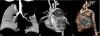
References
-
- Lund JT, Jensen MB, Hjelms E. Aneurysm of the ductus arteriosus.A review of the literature and the surgical implications. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 1991;5:566–70. - PubMed
-
- Varma PK, Vallath G, Neema PK, Sinha PK, Sivadasanpillai H, Menon MU, et al. Clinical profile of post-operative ductal aneurysm and usefulness of sternotomy and circulatory arrest for its repair. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2005;27:416–9. - PubMed
-
- Zilinskas VJ, Maknavicius S, Baliulis G. Successful resection of ductus arteriosus aneurysm in infancy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;69:282–3. - PubMed
-
- Stewart A, Dyamenahalli U, Greenberg SB, Drummond-Webb J. Ductus arteriosus aneurysm with community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection and spontaneous rupture: A potentially fatal quandary. Pediatrics. 2006;117:e1259–62. - PubMed
-
- Dyamenahalli U, Smallhorn JF, Geva T, Fouron JC, Cairns P, Jutras L, et al. Isolated ductus arteriosus aneurysm in the fetus and infant: A multi-institutional experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:262–9. - PubMed

