EWSR1-POU5F1 fusion in soft tissue myoepithelial tumors. A molecular analysis of sixty-six cases, including soft tissue, bone, and visceral lesions, showing common involvement of the EWSR1 gene
- PMID: 20815032
- PMCID: PMC3540416
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.20819
EWSR1-POU5F1 fusion in soft tissue myoepithelial tumors. A molecular analysis of sixty-six cases, including soft tissue, bone, and visceral lesions, showing common involvement of the EWSR1 gene
Abstract
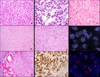
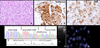
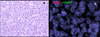
The diagnosis of myoepithelial (ME) tumors outside salivary glands remains challenging, especially in unusual clinical presentations, such as bone or visceral locations. A few reports have indicated EWSR1 gene rearrangement in soft tissue ME tumors, and, in one case each, the fusion partner was identified as either PBX1 or ZNF444. However, larger studies to investigate whether these genetic abnormalities are recurrent or restricted to tumors in soft tissue locations are lacking. Sixty-six ME tumors mainly from soft tissue (71%), but also from skin, bone, and visceral locations, characterized by classic morphological features and supporting immunoprofile were studied. Gene rearrangements in EWSR1, FUS, PBX1, and ZNF444 were investigated by fluorescence in situ hybridization. EWSR1 gene rearrangement was detected in 45% of the cases. A EWSR1-POU5F1 fusion was identified in a pediatric soft tissue tumor by 3'Rapid Amplification of cDNA Euds (RACE) and subsequently confirmed in four additional soft tissue tumors in children and young adults. An EWSR1-PBX1 fusion was seen in five cases, whereas EWSR1-ZNF444 and FUS gene rearrangement was noted in one pulmonary tumor each. In conclusion, EWSR1 gene rearrangement is a common event in ME tumors arising outside salivary glands, irrespective of anatomical location. EWSR1-negative tumors were more often benign, superficially located, and showed ductal differentiation, suggesting the possibility of genetically distinct groups. A subset of soft tissue ME tumors with clear cell morphology harbor an EWSR1-POU5F1 fusion, which can be used as a molecular diagnostic test in difficult cases. These findings do not support a pathogenetic relationship between soft tissue ME tumors and their salivary gland counterparts.
© 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Behboudi A, Enlund F, Winnes M, Andren Y, Nordkvist A, Leivo I, Flaberg E, Szekely L, Makitie A, Grenman R, Mark J, Stenman G. Molecular classification of mucoepidermoid carcinomas-prognostic significance of the MECT1-MAML2 fusion oncogene. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2006;45:470–481. - PubMed
-
- Brandal P, Panagopoulos I, Bjerkehagen B, Gorunova L, Skjeldal S, Micci F, Heim S. Detection of a t(1;22)(q23;q12) translocation leading to an EWSR1-PBX1 fusion gene in a myoepithelioma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2008;47:558–564. - PubMed
-
- Brandal P, Panagopoulos I, Bjerkehagen B, Heim S. t(19;22)(q13;q12) Translocation leading to the novel fusion gene EWSR1-ZNF444 in soft tissue myoepithelial carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2009 - PubMed
-
- Gleason BC, Fletcher CD. Myoepithelial carcinoma of soft tissue in children: an aggressive neoplasm analyzed in a series of 29 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007;31:1813–1824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

