Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases
- PMID: 20815877
- PMCID: PMC2940846
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-232
Cooperative and individualistic functions of the microRNAs in the miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster and its implication in human diseases
Abstract
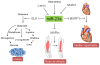
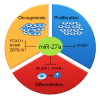
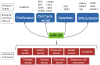
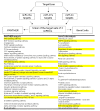
The small RNA molecules of about 19-22 nucleotides in length, aptly called microRNAs, perform the task of gene regulation in the cell. Interestingly, till the early nineties very little was known about them but eventually, the microRNAs have become forefront in the area of research. The huge number of microRNAs plus each one of them targeting a vast number of related as well as unrelated genes makes them very interesting molecules to study. To add to the mystery of miRNAs is the fact that the same miRNA can have antagonizing role in two different cell types i.e. in one cell type; the miRNA promotes proliferation whereas in another cell type the same miRNA inhibits proliferation. Another remarkable aspect of the microRNAs is that many of them exist in clusters. In humans alone, out of 721 microRNAs known, 247 of them occur in 64 clusters at an inter-miRNA distance of less than 5000 bp. The reason for this clustering of miRNAs is not fully understood but since the miRNA clusters are evolutionary conserved, their significance cannot be ruled out. The objective of this review is to summarize the recent progress on the functional characterization of miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster in humans in relation to various health and diseased conditions and to highlight the cooperative effects of the miRNAs of this cluster.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interactive functions of microRNAs in the miR-23a-27a-24-2 cluster and the potential for targeted therapy in cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan;235(1):6-16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28958. Epub 2019 Jun 13. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31192453 Review.
-
Cooperative and Independent Functions of the miR-23a~27a~24-2 Cluster in Bovine Adipocyte Adipogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 9;19(12):3957. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123957. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544847 Free PMC article.
-
MIR-23A microRNA cluster inhibits B-cell development.Exp Hematol. 2010 Aug;38(8):629-640.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.04.004. Epub 2010 May 5. Exp Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20399246 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression profiling indicate role of ER stress in miR-23a~27a~24-2 cluster induced apoptosis in HEK293T cells.RNA Biol. 2011 Jul-Aug;8(4):648-64. doi: 10.4161/rna.8.4.15583. Epub 2011 Jul 1. RNA Biol. 2011. PMID: 21593605
-
Clustered miRNAs and their role in biological functions and diseases.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018 Nov;93(4):1955-1986. doi: 10.1111/brv.12428. Epub 2018 May 24. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018. PMID: 29797774 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells modulate response to experimental sepsis-induced lung injury via regulation of miR-27a-5p in recipient mice.Thorax. 2020 Jul;75(7):556-567. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213561. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Thorax. 2020. PMID: 32546573 Free PMC article.
-
miR-23a promotes the transition from indolent to invasive colorectal cancer.Cancer Discov. 2012 Jun;2(6):540-53. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0267. Epub 2012 Mar 30. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 22628407 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-27a functions as a tumor suppressor in acute leukemia by regulating 14-3-3θ.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050895. Epub 2012 Dec 7. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23236401 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying microRNAs Possibly Implicated in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome and Fibromyalgia: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 3;25(17):9551. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179551. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-23a/27a/24-2 cluster promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation synergistically.Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):2319-2325. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8924. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008935 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

