Eotaxin and FGF enhance signaling through an extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)-dependent pathway in the pathogenesis of Eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 20815913
- PMCID: PMC2976489
- DOI: 10.1186/1710-1492-6-25
Eotaxin and FGF enhance signaling through an extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)-dependent pathway in the pathogenesis of Eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is characterized by the inflammation of the esophagus and the infiltration of eosinophils into the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as dysphagia and stricture formation. Systemic immune indicators like eotaxin and fibroblast growth factor were evaluated for possible synergistic pathological effects. Moreover, blood cells, local tissue, and plasma from EoE and control subjects were studied to determine if the localized disease was associated with a systemic effect that correlated with presence of EoE disease.
Method: Real-time polymerase chain reaction from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), immunohistochemistry from local esophageal biopsies, fluid assays on plasma, and fluorescence-activated cell sorting on peripheral blood cells from subjects were used to study the systemic immune indicators in newly diagnosed EoE (n = 35), treated EoE (n = 9), Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) (n = 8), ulcerative colitis (n = 5), Crohn's disease (n = 5), and healthy controls (n = 8).
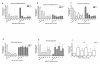
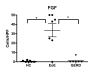
Result: Of the transcripts tested for possible immune indicators, we found extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), Bcl-2, bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor), and eotaxin levels were highly upregulated in PBMC and associated with disease presence of EoE. Increased FGF detected by immunohistochemistry in esophageal tissues and in PBMC was correlated with low levels of pro-apoptotic factors (Fas, Caspase 8) in PBMC from EoE subjects. Plasma-derived bFGF was shown to be the most elevated and most specific in EoE subjects in comparison to healthy controls and disease control subjects.
Conclusion: We describe for the first time a possible mechanism by which increased FGF is associated with inhibiting apoptosis in local esophageal tissues of EoE subjects as compared to controls. Eotaxin and FGF signaling pathways share activation through the ERK pathway; together, they could act to increase eosinophil activation and prolong the half-life of eosinophils in local tissues of the esophagus in EoE subjects.
Figures
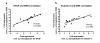
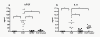


Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical differentiation of eosinophilic esophageal myositis from eosinophilic esophagitis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan;32(1):106-113. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13466. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27262491
-
One-Hour Esophageal String Test: A Nonendoscopic Minimally Invasive Test That Accurately Detects Disease Activity in Eosinophilic Esophagitis.Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct;114(10):1614-1625. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000371. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31567192 Free PMC article.
-
Increased numbers of eosinophils, rather than only etiology, predict histologic changes in patients with esophageal eosinophilia.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012 Jul;10(7):735-41. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2012.01.008. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012. PMID: 22289868
-
Biological Therapies for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Where Do We Stand?Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Oct;55(2):205-216. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8674-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29372536 Review.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: From pathophysiology to treatment.World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 Nov 15;6(4):150-8. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v6.i4.150. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26600973 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Markers of tyrosine kinase activity in eosinophilic esophagitis: a pilot study of the FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion gene, pERK 1/2, and pSTAT5.Dis Esophagus. 2012 Feb;25(2):166-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2011.01230.x. Epub 2011 Aug 5. Dis Esophagus. 2012. PMID: 21819482 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of a Noninvasive Serum Biomarker Panel for Diagnosis and Monitoring of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Prospective Study.Am J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jun;110(6):821-7. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2015.57. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25781367 Free PMC article.
-
FGF2 is overexpressed in asthma and promotes airway inflammation through the FGFR/MAPK/NF-κB pathway in airway epithelial cells.Mil Med Res. 2022 Jan 29;9(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00366-3. Mil Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35093168 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophils in Eosinophilic Esophagitis: The Road to Fibrostenosis is Paved With Good Intentions.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 1;11:603295. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603295. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33335531 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histomorphological and Immunophenotypic Features of Pill-Induced Esophagitis.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 5;10(6):e0128110. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0128110. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26047496 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

