Signaling complexes of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels
- PMID: 20816922
- PMCID: PMC3433163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.085
Signaling complexes of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels
Abstract
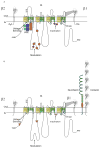
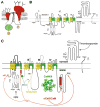
Membrane depolarization and intracellular Ca(2+) transients generated by activation of voltage-gated Na+ and Ca(2+) channels are local signals, which initiate physiological processes such as action potential conduction, synaptic transmission, and excitation-contraction coupling. Targeting of effector proteins and regulatory proteins to ion channels is an important mechanism to ensure speed, specificity, and precise regulation of signaling events in response to local stimuli. This article reviews experimental results showing that Na+ and Ca(2+) channels form local signaling complexes, in which effector proteins, anchoring proteins, and regulatory proteins interact directly with ion channels. The intracellular domains of these channels serve as signaling platforms, mediating their participation in intracellular signaling processes. These protein-protein interactions are important for regulation of cellular plasticity through modulation of Na+ channel function in brain neurons, for short-term synaptic plasticity through modulation of presynaptic Ca(V)2 channels, and for the fight-or-flight response through regulation of postsynaptic Ca(V)1 channels in skeletal and cardiac muscle. These localized signaling complexes are essential for normal function and regulation of electrical excitability, synaptic transmission, and excitation-contraction coupling.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
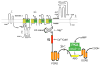
References
-
- Catterall WA. Structure and regulation of voltage-gated calcium channels. Annu Rev Cell Dev Bio. 2000;16:521–555. - PubMed
-
- Cantrell AR, Catterall WA. Neuromodulation of Na+ channels: an unexpected form of cellular plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Scott JD. Signaling through scaffold, anchoring, and adaptor proteins. Science. 1997;278:2075–2080. - PubMed
-
- Qu Y, Curtis R, Lawson D, Gilbride K, Ge P, DiStefano PS, Silos-Santiago I, Catterall WA, Scheuer T. Differential modulation of sodium channel gating and persistent sodium currents by the beta1, beta2, and beta3 subunits. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2001;18:570–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

