Evidence that weakened centromere cohesion is a leading cause of age-related aneuploidy in oocytes
- PMID: 20817534
- PMCID: PMC2939204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.06.069
Evidence that weakened centromere cohesion is a leading cause of age-related aneuploidy in oocytes
Abstract
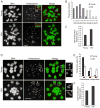
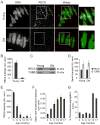
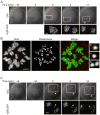
Aneuploidy arising early in development is the leading genetic cause of birth defects and developmental disabilities in humans. Most errors in chromosome number originate from the egg, and maternal age is well established as the key risk factor. Although the importance of this problem for reproductive health is widely recognized, the underlying molecular basis for age-related aneuploidy in female meiosis is unknown. Here we show that weakened chromosome cohesion is a leading cause of aneuploidy in oocytes in a natural aging mouse model. We find that sister kinetochores are farther apart at both metaphase I and II, indicating reduced centromere cohesion. Moreover, levels of the meiotic cohesin protein REC8 are severely reduced on chromosomes in oocytes from old mice. To test whether cohesion defects lead to the observed aneuploidies, we monitored chromosome segregation dynamics at anaphase I in live oocytes and counted chromosomes in the resulting metaphase II eggs. About 90% of age-related aneuploidies are best explained by weakened centromere cohesion. Together, these results demonstrate that the maternal age-associated increase in aneuploidy is often due to a failure to effectively replace cohesin proteins that are lost from chromosomes during aging.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Penrose LS. The relative effects of paternal and maternal age in mongolism. Journal of genetics. 1933;88:9–14. - PubMed
-
- Hassold T, Hunt P. To err (meiotically) is human: the genesis of human aneuploidy. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:280–291. - PubMed
-
- Hassold T, Hall H, Hunt P. The origin of human aneuploidy: where we have been, where we are going. Human molecular genetics. 2007;16(Spec No 2):R203–208. - PubMed
-
- Jones KT. Meiosis in oocytes: predisposition to aneuploidy and its increased incidence with age. Human reproduction update. 2008;14:143–158. - PubMed
-
- Koehler KE, Schrump SE, Cherry JP, Hassold TJ, Hunt PA. Near-human aneuploidy levels in female mice with homeologous chromosomes. Curr Biol. 2006;16:R579–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

