Expression of soluble, active fragments of the morphogenetic protein SpoIIE from Bacillus subtilis using a library-based construct screen
- PMID: 20817757
- PMCID: PMC2953957
- DOI: 10.1093/protein/gzq057
Expression of soluble, active fragments of the morphogenetic protein SpoIIE from Bacillus subtilis using a library-based construct screen
Abstract
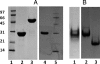
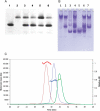
SpoIIE is a dual function protein that plays important roles during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. It binds to the tubulin-like protein FtsZ causing the cell division septum to relocate from mid-cell to the cell pole, and it dephosphorylates SpoIIAA phosphate leading to establishment of differential gene expression in the two compartments following the asymmetric septation. Its 872 residue polypeptide contains a multiple-membrane spanning sequence at the N-terminus and a PP2C phosphatase domain at the C-terminus. The central segment that binds to FtsZ is unlike domains of known structure or function, moreover the domain boundaries are poorly defined and this has hampered the expression of soluble fragments of SpoIIE at the levels required for structural studies. Here we have screened over 9000 genetic constructs of spoIIE using a random incremental truncation library approach, ESPRIT, to identify a number of soluble C-terminal fragments of SpoIIE that were aligned with the protein sequence to map putative domains and domain boundaries. The expression and purification of three fragments were optimised, yielding multimilligram quantities of the PP2C phosphatase domain, the putative FtsZ-binding domain and a larger fragment encompassing both these domains. All three fragments are monomeric and the PP2C domain-containing fragments have phosphatase activity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure of the phosphatase domain of the cell fate determinant SpoIIE from Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 13;415(2):343-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.017. Epub 2011 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22115775 Free PMC article.
-
Metal-dependent SpoIIE oligomerization stabilizes FtsZ during asymmetric division in Bacillus subtilis.PLoS One. 2017 Mar 30;12(3):e0174713. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0174713. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28358838 Free PMC article.
-
The cell differentiation protein SpoIIE contains a regulatory site that controls its phosphatase activity in response to asymmetric septation.Mol Microbiol. 2002 Aug;45(4):1119-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03082.x. Mol Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12180929
-
Control of the cell-specificity of sigma F activity in Bacillus subtilis.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Apr 29;351(1339):537-42. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0052. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996. PMID: 8735276 Review.
-
Cell Cycle Machinery in Bacillus subtilis.Subcell Biochem. 2017;84:67-101. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-53047-5_3. Subcell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28500523 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphogenic Protein RodZ Interacts with Sporulation Specific SpoIIE in Bacillus subtilis.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 14;11(7):e0159076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159076. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27415800 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the phosphatase domain of the cell fate determinant SpoIIE from Bacillus subtilis.J Mol Biol. 2012 Jan 13;415(2):343-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2011.11.017. Epub 2011 Nov 15. J Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22115775 Free PMC article.
-
Linking the Peptidoglycan Synthesis Protein Complex with Asymmetric Cell Division during Bacillus subtilis Sporulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 25;21(12):4513. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124513. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630428 Free PMC article.
-
Library methods for structural biology of challenging proteins and their complexes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013 Jun;23(3):403-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2013.03.004. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2013. PMID: 23602357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CoESPRIT: a library-based construct screening method for identification and expression of soluble protein complexes.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 22;6(2):e16261. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016261. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21364980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelini A., Tosi T., Mas P., Acajjaoui S., Zanotti G., Terradot L., Hart D.J. FEBS J. 2009;276:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Arigoni F., Pogliano K., Webb C.D., Stragier P., Losick R. Science. 1995;270:637–640. - PubMed
-
- Arigoni F., Guerout-Fleury A.M., Barak I., Stragier P. Mol. Microbiol. 1999;31:1407–1415. - PubMed
-
- Barak I., Behari J., Olmedo G., Guzman P., Brown D.P., Castro E., Walker D., Westpheling J., Youngman P. Mol. Microbiol. 1996;19:1047–1060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

