Extracellular transsulfuration generates hydrogen sulfide from homocysteine and protects endothelium from redox stress
- PMID: 20817827
- PMCID: PMC2993215
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00555.2010
Extracellular transsulfuration generates hydrogen sulfide from homocysteine and protects endothelium from redox stress
Abstract
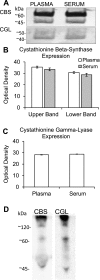
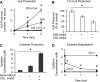
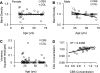
Homocysteine, a cardiovascular and neurocognitive disease risk factor, is converted to hydrogen sulfide, a cardiovascular and neuronal protectant, through the transsulfuration pathway. Given the damaging effects of free homocysteine in the blood and the importance of blood homocysteine concentration as a prognosticator of disease, we tested the hypotheses that the blood itself regulates homocysteine-hydrogen sulfide metabolism through transsulfuration and that transsulfuration capacity and hydrogen sulfide availability protect the endothelium from redox stress. Here we show that the transsulfuration enzymes, cystathionine β-synthase and cystathionine γ-lyase, are secreted by microvascular endothelial cells and hepatocytes, circulate as members of the plasma proteome, and actively produce hydrogen sulfide from homocysteine in human blood. We further demonstrate that extracellular transsulfuration regulates cell function when the endothelium is challenged with homocysteine and that hydrogen sulfide protects the endothelium from serum starvation and from hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. These novel findings uncover a unique set of opportunities to explore innovative clinical diagnostics and therapeutic strategies in the approach to homocysteine-related conditions such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and dementia.
Figures





References
-
- American Medical Association Homocysteine, and risk of ischemic heart disease and stroke: a meta-analysis. J Am Med Assoc 288: 2015– 2022, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen JD, Jensen LJ, Blom N, Von Heijne G, Brunak S. Feature-based prediction of non-classical and leaderless protein secretion. Protein Eng Des Sel 17: 349– 356, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Blackstone E, Morrison M, Roth MB. H2S induces a suspended animation-like state in mice (Abstract). Science 308: 518, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Chambers JC, Ueland PM, Wright M, Dore CJ, Refsum H, Kooner JS. Investigation of relationship between reduced, oxidized, and protein-bound homocysteine and vascular endothelial function in healthy human subjects. Circ Res 89: 187– 192, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

