Proteomic and functional analysis of the mitotic Drosophila centrosome
- PMID: 20818332
- PMCID: PMC2957212
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.210
Proteomic and functional analysis of the mitotic Drosophila centrosome
Abstract
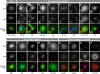
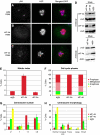
Regulation of centrosome structure, duplication and segregation is integrated into cellular pathways that control cell cycle progression and growth. As part of these pathways, numerous proteins with well-established non-centrosomal localization and function associate with the centrosome to fulfill regulatory functions. In turn, classical centrosomal components take up functional and structural roles as part of other cellular organelles and compartments. Thus, although a comprehensive inventory of centrosome components is missing, emerging evidence indicates that its molecular composition reflects the complexity of its functions. We analysed the Drosophila embryonic centrosomal proteome using immunoisolation in combination with mass spectrometry. The 251 identified components were functionally characterized by RNA interference. Among those, a core group of 11 proteins was critical for centrosome structure maintenance. Depletion of any of these proteins in Drosophila SL2 cells resulted in centrosome disintegration, revealing a molecular dependency of centrosome structure on components of the protein translation machinery, actin- and RNA-binding proteins. In total, we assigned novel centrosome-related functions to 24 proteins and confirmed 13 of these in human cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

