The inhibitory effects of intravenous administration of rabbit immunoglobulin G on airway inflammation are dependent upon Fcγ receptor IIb on CD11c(+) dendritic cells in a murine model
- PMID: 20819092
- PMCID: PMC2996599
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04243.x
The inhibitory effects of intravenous administration of rabbit immunoglobulin G on airway inflammation are dependent upon Fcγ receptor IIb on CD11c(+) dendritic cells in a murine model
Abstract
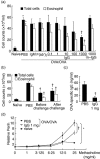
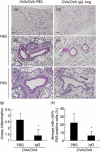
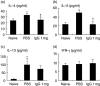
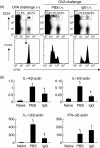
Immunoglobulins (Igs) play important immunomodulatory effects on allergic asthma. Among these, IgG has been reported to regulate allergic inflammation in previous studies about immunotherapy and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. In this study, to examine the immunomodulatory mechanisms of IgG and FcRs we evaluated the effects of intravenous (i.v.) rabbit IgG administration (IVIgG) on allergic airway inflammation and lung antigen-presenting cells (APCs) in a murine model of ovalbumin (OVA) sensitization and challenge. In OVA-challenged mice, IVIgG attenuated airway eosinophilia, airway hyperresponsiveness and goblet cell hyperplasia and also inhibited the local T helper type (Th) 2 cytokine levels. Additionally, IVIgG attenuated the proliferation of OVA-specific CD4(+) T cells transplanted into OVA-challenged mice. Ex vivo co-culture with OVA-specific CD4(+) cells and lung CD11c(+) APCs from mice with IVIgG revealed the attenuated transcription level of Th2 cytokines, suggesting an inhibitory effect of IVIgG on CD11c(+) APCs to induce Th2 response. Next, to analyse the effects on Fcγ receptor IIb and dendritic cells (DCs), asthmatic features in Fcγ receptor IIb-deficient mice were analysed. IVIgG failed to attenuate airway eosinophilia, airway inflammation and goblet cell hyperplasia. However, the lacking effects of IVIgG on airway eosinophilia in Fcγ receptor IIb deficiency were restored by i.v. transplantation of wild-type bone marrow-derived CD11c(+) DCs. These results demonstrate that IVIgG attenuates asthmatic features and the function of lung CD11c(+) DCs via Fcγ receptor IIb in allergic airway inflammation. Targeting Fc portions of IgG and Fcγ receptor IIb on CD11c(+) DCs in allergic asthma is a promising therapeutic strategy.
© 2010 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
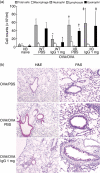
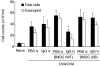
References
-
- Wills-Karp M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:255–81. - PubMed
-
- Djukanovic R, Wilson SJ, Kraft M, et al. Effects of treatment with anti-immunoglobulin E antibody omalizumab on airway inflammation in allergic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170:583–93. - PubMed
-
- Muller U, Akdis CA, Fricker M, et al. Successful immunotherapy with T-cell epitope peptides of bee venom phospholipase A2 induces specific T-cell anergy in patients allergic to bee venom. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1998;101:747–54. - PubMed
-
- Haque S, Boyce N, Thien FC, O'Hehir RE, Douglass J. Role of intravenous immunoglobulin in severe steroid-dependent asthma. Intern Med J. 2003;33:341–4. - PubMed
-
- Salmun LM, Barlan I, Wolf HM, et al. Effect of intravenous immunoglobulin on steroid consumption in patients with severe asthma: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;103:810–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

