Extracerebral metastases determine the outcome of patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 20819239
- PMCID: PMC2942853
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-480
Extracerebral metastases determine the outcome of patients with brain metastases from renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: In the era of cytokines, patients with brain metastases (BM) from renal cell carcinoma had a significantly shorter survival than patients without. Targeted agents (TA) have improved the outcome of patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) however, their impact on patients with BM is less clear. The aim of this analysis was to compare the outcome of patients with and without BM in the era of targeted agents.
Methods: Data from 114 consecutive patients who had access to targeted agent were analyzed for response rates (ORR), progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). All patients diagnosed with BM underwent local, BM-specific treatment before initiation of medical treatment.
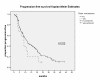
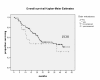
Results: Data of 114 consecutive patients who had access to at least one type of targeted agents were analyzed. Twelve out of 114 renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients (10.5%) were diagnosed with BM. Systemic treatment consisted of sunitinib, sorafenib, temsirolimus or bevacizumab. The median PFS was 8.7 months (95% CI 5.1 - 12.3) and 11.4 months (95% CI 8.7 - 14.1) for BM-patients and non-BM-patients, respectively (p = 0.232). The median overall survival for patients with and without BM was 13.4 (95% CI 1- 43.9) and 33.3 months (95% CI 18.6 - 47.0) (p = 0.358), respectively. No patient died from cerebral disease progression. ECOG Performance status and the time from primary tumor to metastases (TDM) were independent risk factors for short survival (HR 2.74, p = 0.001; HR: 0.552, p = 0.034).
Conclusions: Although extracerebral metastases determine the outcome of patients with BM, the benefit from targeted agents still appears to be limited when compared to patients without BM.
Figures
References
-
- Sheehan JP, Sun MH, Kondziolka D, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD. Radiosurgery in patients with renal cell carcinoma metastasis to the brain: long-term outcomes and prognostic factors influencing survival and local tumor control. J Neurosurg. 2003;98(2):342–349. doi: 10.3171/jns.2003.98.2.0342. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clarke JW, Register S, McGregor JM, Grecula JC, Mayr NA, Wang JZ, Li K, Gupta N, Kendra KL, Olencki TE, Cavaliere R, Sarkar A, Lo SS. Stereotactic Radiosurgery With or Without Whole Brain Radiotherapy for Patients With a Single Radioresistant Brain Metastasis. Am J Clin Oncol. 2009. - PubMed
-
- Marko NF, Angelov L, Toms SA, Suh JH, Chao ST, Vogelbaum MA, Barnett GH, Weil RJ. Stereotactic radiosurgery as single-modality treatment of incidentally identified renal cell carcinoma brain metastases. Surg Neurol. 2009. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

