Comparison of carbon dioxide and argon euthanasia: effects on behavior, heart rate, and respiratory lesions in rats
- PMID: 20819391
- PMCID: PMC2919185
Comparison of carbon dioxide and argon euthanasia: effects on behavior, heart rate, and respiratory lesions in rats
Abstract
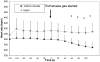
In this study we compared rat (n = 16) responses to euthanasia with either gradual-fill CO(2) or rapid induction argon gas by evaluating the animals' heart rate via radiotelemetry, behavior, and vocalizations. We also evaluated the histologic effects of the gases. Rats were placed in an open test chamber 24 h before the start of the experiment. During baseline tests, rats were exposed to oxygen to evaluate the effects of the noise and movement of gas entering the chamber; 1 wk later, rats were euthanized by gas displacement with either 10%/min CO(2) or 50%/min argon gas. Rats tended to have higher heart rats and were more active during the baseline test, but these parameters were normal before the euthanasia experiment, suggesting that the rats had acclimated to the equipment. Heart rate, behavior, and ultrasonic vocalizations were recorded for 2 min after gas introduction in both groups. All rats appeared conscious throughout the test interval. The heart rates of rats exposed to argon did not change, whereas those of rats exposed to CO(2) declined significantly. Unlike those exposed to CO(2), rats euthanized with argon gas gasped and demonstrated seizure-like activity. There were no differences in the pulmonary lesions resulting from death by either gas. Our results suggest that argon as a sole euthanasia agent is aversive to rats. CO(2) using a 10%/min displacement may be less aversive than more rapid displacements. Future research investigating methods of euthanasia should allow sufficient time for the rats to acclimate to the test apparatus.
Figures

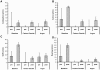
References
-
- Altland PD, Brubach HF, Parker MG. 1968. Effects of inert gasses on tolerance of rats to hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 24:778–781 - PubMed
-
- American Veterinary Medical Association 2001. 2000 report of the AVMA panel on euthanasia. J Am Vet Med Assoc 218:669–696 - PubMed
-
- Anton F, Euchner I, Handwerker HO. 1992. Psychophysical examination of pain induced by defined CO2 pulses applied to the nasal mucosa. Pain 49:53–60 - PubMed
-
- Anton F, Peppel P, Euchner I, Handwerker HO. 1991. Controlled noxious chemical stimulation: responses of rat trigeminal brainstem neurones to CO2 pulses applied to the nasal mucosa. Neurosci Lett 123:208–211 - PubMed
-
- Azar T, Sharp J, Lawson D. 2005. Stress-like cardiovascular respnses to common procedures in male versus female spontaneously hypertensive rats. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci 44:25–30 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
