Expression of lumican in the articular disc of the human temporomandibular joint
- PMID: 20819773
- PMCID: PMC3167310
- DOI: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e34
Expression of lumican in the articular disc of the human temporomandibular joint
Abstract
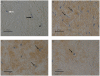
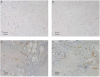
Lumican belongs to the small leucine-rich repeat proteoglycan (SLRP) gene family and has been reported to exist in the cornea, intervertebral disc and tendon. Lumican plays a significant role in the assembly and regulation of collagen fibres. The human temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disc is made up of fibrocartilage with an extracellular matrix (ECM) composed of collagen and proteoglycans. The existence and behaviour of lumican has not been studied in the human TMJ disc. Therefore, we used immunohistochemical methods to detect lumican, CD34 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and histochemical staining with toluidine blue in 13 human TMJ specimens (10 surgically removed and 3 obtained from autopsy). In both the normal and the deformed discs we observed staining with toluidine blue. We found that the area of metachromasia inside the deformed disc was uneven and expression of lumican was strong in the areas negative for metachromasia. Staining of VEGF and CD34 inside the deformed disc was seen. We confirmed the expression of lumican in the human TMJ disc and showed that a large number of fibroblast-like cells existed in the area of strong lumican expression. These new findings about the behaviour of lumican suggest that it may play a key role in the generation of a new collagen network by fibroblast-like cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of lumican and fibromodulin following interleukin-1 beta stimulation of disc cells of the human temporomandibular joint.Eur J Histochem. 2011;55(2):e11. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e11. Eur J Histochem. 2011. PMID: 22073367 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of interleukin-1beta and dehydroepiandrosterone on the expression of lumican and fibromodulin in fibroblast-like synovial cells of the human temporomandibular joint.Eur J Histochem. 2015 Feb 23;59(1):2440. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2015.2440. Eur J Histochem. 2015. PMID: 25820556 Free PMC article.
-
Proteoglycan expression is influenced by mechanical load in TMJ discs.J Dent Res. 2015 Jan;94(1):93-100. doi: 10.1177/0022034514553816. Epub 2014 Oct 27. J Dent Res. 2015. PMID: 25348543
-
Histochemistry for studying structure and function of the articular disc of the human temporomandibular joint.Eur J Histochem. 2012 Feb 29;56(1):e11. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2012.e11. Eur J Histochem. 2012. PMID: 22472889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of SLRP-proteoglycans in osteosarcoma pathogenesis.Connect Tissue Res. 2008;49(3):235-8. doi: 10.1080/03008200802147589. Connect Tissue Res. 2008. PMID: 18661350 Review.
Cited by
-
Low-level laser therapy stimulates tissue repair and reduces the extracellular matrix degradation in rats with induced arthritis in the temporomandibular joint.Lasers Med Sci. 2016 Aug;31(6):1051-9. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-1946-3. Epub 2016 May 4. Lasers Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27147076
-
Expression of hyaluronan synthase 3 in deformed human temporomandibular joint discs: in vivo and in vitro studies.Eur J Histochem. 2010 Dec 15;54(4):e50. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e50. Eur J Histochem. 2010. PMID: 21263749 Free PMC article.
-
Synovial Tissue Proteins and Patient-Specific Variables as Predictive Factors for Temporomandibular Joint Surgery.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;11(1):46. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11010046. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396653 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying pathological biomarkers: histochemistry still ranks high in the omics era.Eur J Histochem. 2011 Dec 7;55(4):e42. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e42. Eur J Histochem. 2011. PMID: 22297448 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical expression of types I and III collagen antibodies in the temporomandibular joint disc of human foetuses.Eur J Histochem. 2011;55(3):e24. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e24. Epub 2011 Aug 27. Eur J Histochem. 2011. PMID: 22073371 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Funderburgh JL, Funderburgh ML, Mann MM, Conrad GW. Arterial lumican. Properties of a corneal-type keratan sulfate proteoglycan from bovine aorta. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:24773–7. - PubMed
-
- Blochberger TC, Vergnes J, Hempel J, Hassell JR. cDNA to chick lumican (corneal keratan sulfate proteoglycan) reveals homology to the small interstitial proteoglycan gene family and expression in muscle and intestine. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:347–52. - PubMed
-
- Nikitovic D, Katonis P, Tsatsakis A, Karamanos NK, Tzanakakis GN. Lumican, a small leucine-rich proteoglycan. IUBMB Life. 2008;12:818–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

