An integrated genomic analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated inhibition of B-cell differentiation
- PMID: 20819909
- PMCID: PMC3003543
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq265
An integrated genomic analysis of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated inhibition of B-cell differentiation
Abstract
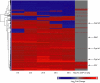
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) alters differentiation of B cells and suppresses antibody production. A combination of whole-genome, microarray-based chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP-on-chip), and time course gene expression microarray analysis was performed on the mouse B-cell line CH12.LX following exposure to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or LPS and TCDD to identify the primary and downstream transcriptional elements of B-cell differentiation that are altered by the AHR. ChIP-on-chip analysis identified 1893 regions with a significant increase in AHR binding with TCDD treatment. Transcription factor binding site analysis on the ChIP-on-chip data showed enrichment in AHR response elements. Other transcription factors showed significant coenrichment with AHR response elements. When ChIP-on-chip regions were compared with gene expression changes at the early time points, 78 genes were identified as potential direct targets of the AHR. AHR binding and expression changes were confirmed for a subset of genes in primary mouse B cells. Network analysis examining connections between the 78 potential AHR target genes and three transcription factors known to regulate B-cell differentiation indicated multiple paths for potential regulation by the AHR. Enrichment analysis on the differentially expressed genes at each time point evaluated the downstream impact of AHR-regulated gene expression changes on B-cell-related processes. AHR-mediated impairment of B-cell differentiation occurred at multiple nodes of the B-cell differentiation network and potentially through multiple mechanisms including direct cis-acting effects on key regulators of B-cell differentiation, indirect regulation of B-cell differentiation-related pathways, and transcriptional coregulation of target genes by AHR and other transcription factors.
Figures







References
-
- Barhoover MA, Hall JM, Greenlee WF, Thomas RS. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates cell cycle progression in human breast cancer cells via a functional interaction with cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010;77:195–201. - PubMed
-
- Battistini A. Interferon regulatory factors in hematopoietic cell differentiation and immune regulation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009;29:765–780. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Calame K. Activation-dependent induction of Blimp-1. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2008;20:259–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

