MRI of retinal and choroidal blood flow with laminar resolution
- PMID: 20821409
- PMCID: PMC3026903
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.1576
MRI of retinal and choroidal blood flow with laminar resolution
Abstract
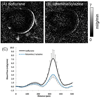
The retina is nourished by two distinct circulations: the retinal vessels within the inner retina and the choroidal vessels behind the neural retina. The outer nuclear layer and the inner and outer segments of the photoreceptors in between are avascular. The aim of this study was to determine whether arterial spin labeling MRI could provide sufficient resolution to differentiate between quantitative retinal blood flow (rBF) and choroidal blood flow (chBF), and whether this technique is sufficiently sensitive to detect vascular-specific blood flow (BF) changes modulated by anesthetics. Arterial spin labeling MRI was performed at 42 × 42 × 400 µm(3) in the mouse retina at 7 T, and was used to investigate the effects of isoflurane and ketamine/xylazine anesthesia on rBF and chBF. MRI yielded unambiguous differentiation of rBF, chBF and the avascular layer in between. Under isoflurane, chBF was 7.7 ± 2.1 mL/g/min and rBF was 1.3 ± 0.44 mL/g/min (mean ± SD, n = 7, p < 0.01). Under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia in the same animals, chBF was 4.3 ± 1.9 mL/g/min and rBF was 0.88 ± 0.22 mL/g/min (p < 0.01). Under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia, rBF was lower by 29% (P < 0.01) and chBF by 42% (P < 0.01) relative to isoflurane. This study demonstrates, for the first time, the quantitative imaging of rBF and chBF in vivo, providing a new method to study basal values and alterations of rBF and chBF.
Copyright © 2010 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diabetic mice have retinal and choroidal blood flow deficits and electroretinogram deficits with impaired responses to hypercapnia.PLoS One. 2021 Dec 9;16(12):e0259505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259505. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34882677 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the superior salivatory nucleus in parasympathetic control of choroidal blood flow and in maintenance of retinal health.Exp Eye Res. 2021 May;206:108541. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108541. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33736985 Free PMC article.
-
Defective Choroidal Blood Flow Baroregulation and Retinal Dysfunction and Pathology Following Sympathetic Denervation of Choroid.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Oct 1;59(12):5032-5044. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-24954. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 30326072 Free PMC article.
-
Oxygen distribution and consumption within the retina in vascularised and avascular retinas and in animal models of retinal disease.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001 Mar;20(2):175-208. doi: 10.1016/s1350-9462(00)00027-6. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2001. PMID: 11173251 Review.
-
Neural control of choroidal blood flow.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018 May;64:96-130. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29229444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance imaging of the retina: from mice to men.Magn Reson Med. 2014 Apr;71(4):1526-30. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24797. Epub 2013 May 28. Magn Reson Med. 2014. PMID: 23716429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lamina-specific anatomic magnetic resonance imaging of the human retina.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011 Sep 14;52(10):7232-7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-7623. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21828153 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of retinal and cerebral blood flow between continuous arterial spin labeling MRI and fluorescent microsphere techniques.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014 Sep;40(3):609-15. doi: 10.1002/jmri.24407. Epub 2013 Nov 13. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24227681 Free PMC article.
-
3D magnetic resonance microscopy of the ex vivo retina.Magn Reson Med. 2012 Apr;67(4):1154-8. doi: 10.1002/mrm.23082. Epub 2011 Oct 18. Magn Reson Med. 2012. PMID: 22009721 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin 50 Influences the Physiological Optics of the In Vivo Mouse Lens.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Jul 1;65(8):19. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.8.19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38984874 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cioffi GA, Granstam E, Alm A. Ocular Circulation. In: Kaufman PL, Alm A, editors. Adler’s Physiology of the Eye. 10th ed. St. Louis, MO: Mosby; 2003. pp. 747–773.
-
- Chen J, Wang Q, Zhang J, Yang X, Wang J, Berkowitz BA, Wickline SA, Song SK. In vivo quantification of T1, T2, and apparent diffusion coefficient in the mouse retina at 11.74T. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 2008;59:731–738. - PubMed
-
- Roth S. The effects of halothane on retinal and choroidal blood flow in cats. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:455–460. - PubMed
-
- Tilton RG, Chang K, Weigel C, Eades D, Sherman WR, Kilo C, Williamson JR. Increased ocular blood flow and 125I-albumin permeation in galactose-fed rats: inhibition by sorbinil. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1988;29:861–868. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

