A large proportion of asymptomatic Plasmodium infections with low and sub-microscopic parasite densities in the low transmission setting of Temotu Province, Solomon Islands: challenges for malaria diagnostics in an elimination setting
- PMID: 20822506
- PMCID: PMC2944341
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-9-254
A large proportion of asymptomatic Plasmodium infections with low and sub-microscopic parasite densities in the low transmission setting of Temotu Province, Solomon Islands: challenges for malaria diagnostics in an elimination setting
Abstract
Background: Many countries are scaling up malaria interventions towards elimination. This transition changes demands on malaria diagnostics from diagnosing ill patients to detecting parasites in all carriers including asymptomatic infections and infections with low parasite densities. Detection methods suitable to local malaria epidemiology must be selected prior to transitioning a malaria control programme to elimination. A baseline malaria survey conducted in Temotu Province, Solomon Islands in late 2008, as the first step in a provincial malaria elimination programme, provided malaria epidemiology data and an opportunity to assess how well different diagnostic methods performed in this setting.
Methods: During the survey, 9,491 blood samples were collected and examined by microscopy for Plasmodium species and density, with a subset also examined by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs). The performances of these diagnostic methods were compared.
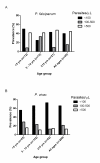
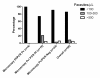
Results: A total of 256 samples were positive by microscopy, giving a point prevalence of 2.7%. The species distribution was 17.5% Plasmodium falciparum and 82.4% Plasmodium vivax. In this low transmission setting, only 17.8% of the P. falciparum and 2.9% of P. vivax infected subjects were febrile (≥ 38°C) at the time of the survey. A significant proportion of infections detected by microscopy, 40% and 65.6% for P. falciparum and P. vivax respectively, had parasite density below 100/μL. There was an age correlation for the proportion of parasite density below 100/μL for P. vivax infections, but not for P. falciparum infections. PCR detected substantially more infections than microscopy (point prevalence of 8.71%), indicating a large number of subjects had sub-microscopic parasitemia. The concordance between PCR and microscopy in detecting single species was greater for P. vivax (135/162) compared to P. falciparum (36/118). The malaria RDT detected the 12 microscopy and PCR positive P. falciparum, but failed to detect 12/13 microscopy and PCR positive P. vivax infections.
Conclusion: Asymptomatic malaria infections and infections with low and sub-microscopic parasite densities are highly prevalent in Temotu province where malaria transmission is low. This presents a challenge for elimination since the large proportion of the parasite reservoir will not be detected by standard active and passive case detection. Therefore effective mass screening and treatment campaigns will most likely need more sensitive assays such as a field deployable molecular based assay.
Figures
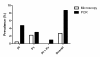
Similar articles
-
Microscopic and molecular evidence of the presence of asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax infections in an area with low, seasonal and unstable malaria transmission in Ethiopia.BMC Infect Dis. 2015 Aug 5;15:310. doi: 10.1186/s12879-015-1070-1. BMC Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26242405 Free PMC article.
-
Submicroscopic carriage of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in a low endemic area in Ethiopia where no parasitaemia was detected by microscopy or rapid diagnostic test.Malar J. 2015 Aug 5;14:303. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0821-1. Malar J. 2015. PMID: 26242243 Free PMC article.
-
The detection of cryptic Plasmodium infection among villagers in Attapeu province, Lao PDR.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017 Dec 20;11(12):e0006148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006148. eCollection 2017 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017. PMID: 29261647 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis: rapid diagnostic tests versus placental histology, microscopy and PCR for malaria in pregnant women.Malar J. 2011 Oct 28;10:321. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-321. Malar J. 2011. PMID: 22035448 Free PMC article.
-
Summary of discordant results between rapid diagnosis tests, microscopy, and polymerase chain reaction for detecting Plasmodium mixed infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 29;10(1):12765. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-69647-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32728145 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Large Plasmodium vivax Reservoir and Little Population Structure in the South Pacific.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 18;8(6):e66041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066041. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23823758 Free PMC article.
-
The complexities of malaria disease manifestations with a focus on asymptomatic malaria.Malar J. 2012 Jan 31;11:29. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-29. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 22289302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimation of Plasmodium falciparum Transmission Intensity in Lilongwe, Malawi, by Microscopy, Rapid Diagnostic Testing, and Nucleic Acid Detection.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016 Aug 3;95(2):373-7. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0156. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2016. PMID: 27325802 Free PMC article.
-
The role of submicroscopic parasitemia in malaria transmission: what is the evidence?Trends Parasitol. 2014 Apr;30(4):183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2014.02.004. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Trends Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24642035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiplexed Microsphere-Based Flow Cytometric Assay to Assess Strain Transcending Antibodies to Plasmodium vivax Duffy Binding Protein II Reveals an Efficient Tool to Identify Binding-Inhibitory Antibody Responders.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 5;12:704653. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.704653. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34675915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wongsrichanalai C, Barcus MJ, Muth S, Sutamihardja A, Wernsdorfer WH. A review of malaria diagnostic tools: microscopy and rapid diagnostic test (RDT) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007;77(6 Suppl):119–127. - PubMed
-
- Snounou G, Viriyakosol S, Jarra W, Thaithong S, Brown KN. Identification of the four human malaria parasite species in field samples by the polymerase chain reaction and detection of a high prevalence of mixed infections. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1993;58:283–292. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)90050-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

