Angiopoietin-4 promotes glioblastoma progression by enhancing tumor cell viability and angiogenesis
- PMID: 20823154
- PMCID: PMC2940950
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4125
Angiopoietin-4 promotes glioblastoma progression by enhancing tumor cell viability and angiogenesis
Abstract
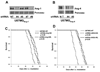
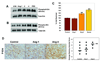
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a highly invasive and vascularized aggressive brain tumor. Less than 10% of GBM patients survive >5 years after diagnosis. Angiogenesis plays an important role in GBM growth, and antiangiogenesis-based therapies have shown clinical efficacy for GBM patients. Unfortunately, therapeutic resistance often develops in these patients, suggesting that GBM cells are capable of switching their dependency on one proangiogenic signaling pathway to an alternative one. Therefore, it is important to identify novel angiogenic factors that play essential roles in tumor angiogenesis and GBM progression. Angiopoietins (Ang-1, Ang-2, and Ang-4) are the ligands of the Tie-2 receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). The roles of Ang-1 and Ang-2 in tumor angiogenesis have been established. However, little is known about how Ang-4 affects tumor angiogenesis and GBM progression and the mechanism underlying its effects. In our current study, we establish that Ang-4 is upregulated in human GBM tissues and cells. We show that, like endothelial cells, human GBM cells express Tie-2 RTK. We first establish that Ang-4 promotes in vivo growth of human GBM cells by promoting tumor angiogenesis and directly activating extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (Erk1/2) in GBM cells. Our results establish the novel effects of Ang-4 on tumor angiogenesis and GBM progression and suggest that this pro-GBM effect of Ang-4 is mediated by promoting tumor angiogenesis and activating Erk1/2 kinase in GBM cells. Together, our results suggest that the Ang-4-Tie-2 functional axis is an attractive therapeutic target for GBM.
©2010 AACR.
Figures
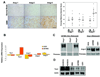
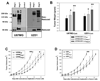
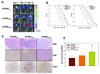
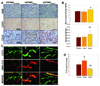
Similar articles
-
Angiopoietin-3 inhibits pulmonary metastasis by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis.Cancer Res. 2004 Sep 1;64(17):6119-26. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1054. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15342395
-
Effects of tumor suppressor gene (p53) on brain tumor angiogenesis and expression of angiogenic modulators.Anticancer Res. 2004 Jan-Feb;24(1):1-10. Anticancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15015569
-
Aspirin Affects Tumor Angiogenesis and Sensitizes Human Glioblastoma Endothelial Cells to Temozolomide, Bevacizumab, and Sunitinib, Impairing Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Related Signaling.World Neurosurg. 2018 Dec;120:e380-e391. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.08.080. Epub 2018 Aug 23. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 30144594
-
Tie-1: A potential target for anti-angiogenesis therapy.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015 Oct;35(5):615-622. doi: 10.1007/s11596-015-1479-1. Epub 2015 Oct 22. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26489611 Review.
-
Angiopoietins in angiogenesis.Cancer Lett. 2013 Jan 1;328(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.08.018. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 22922303 Review.
Cited by
-
Glioblastoma at the crossroads: current understanding and future therapeutic horizons.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Jul 9;10(1):213. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02299-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40628732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merlin is a negative regulator of human melanoma growth.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43295. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043295. Epub 2012 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22912849 Free PMC article.
-
Stromal-epithelial crosstalk provides a suitable microenvironment for the progression of ovarian cancer cells in vitro.Cancer Invest. 2013 Nov;31(9):616-24. doi: 10.3109/07357907.2013.849723. Epub 2013 Oct 22. Cancer Invest. 2013. PMID: 24147897 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoid-Mediated Suppression of Tumor Angiogenesis: Roles of Ang-Tie/PI3K/AKT.Pathophysiology. 2024 Oct 12;31(4):596-607. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31040043. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39449525 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Vascular Microenvironment in Glioblastoma: A Comprehensive Review.Biomedicines. 2022 May 31;10(6):1285. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061285. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY. Novel anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol. 2008;7:1152–1160. - PubMed
-
- Norden AD, Drappatz J, Wen PY. Antiangiogenic therapy in malignant gliomas. Curr Opin Oncol. 2008;20:652–661. - PubMed
-
- Norden AD, Young GS, Setayesh K, et al. Bevacizumab for recurrent malignant gliomas: efficacy, toxicity, and patterns of recurrence. Neurology. 2008;70:779–787. - PubMed
-
- Masabumi S. Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: therapeutic aspects of vascular endothelial growth factor. FEBS Journal. 2009;276:4636–4643. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

