Development of two animal models to study the function of Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems
- PMID: 20823199
- PMCID: PMC2976342
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00461-10
Development of two animal models to study the function of Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems
Abstract
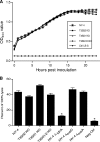
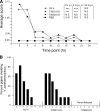
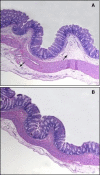
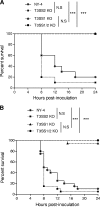
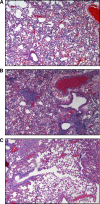
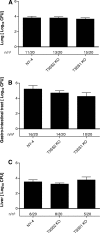
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is an emerging food- and waterborne pathogen that encodes two type III secretion systems (T3SSs). Previous studies have linked type III secretion system 1 (T3SS1) to cytotoxicity and T3SS2 to intestinal fluid accumulation, but animal challenge models needed to study these phenomena are limited. In this study we evaluated the roles of the T3SSs during infection using two novel animal models: a model in which piglets were inoculated orogastrically and a model in which mice were inoculated in their lungs (intrapulmonarily). The bacterial strains employed in this study had equivalent growth rates and beta-hemolytic activity based on in vitro assays. Inoculation of 48-h-old conventional piglets with 10(11) CFU of the wild-type strain (NY-4) or T3SS1 deletion mutant strains resulted in acute, self-limiting diarrhea, whereas inoculation with a T3SS2 deletion mutant strain failed to produce any clinical symptoms. Intrapulmonary inoculation of C57BL/6 mice with the wild-type strain and T3SS2 deletion mutant strains (5 × 10(5) CFU) induced mortality or a moribund state within 12 h (80 to 100% mortality), whereas inoculation with a T3SS1 deletion mutant or a T3SS1 T3SS2 double deletion mutant produced no mortality. Bacteria were recovered from multiple organs regardless of the strain used in the mouse model, indicating that the mice were capable of clearing the lung infection in the absence of a functional T3SS1. Because all strains had a similar beta-hemolysin phenotype, we surmise that thermostable direct hemolysin (TDH) plays a limited role in these models. The two models introduced herein produce robust results and provide a means to determine how different T3SS1 and T3SS2 effector proteins contribute to pathogenesis of V. parahaemolyticus infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contribution of Vibrio parahaemolyticus virulence factors to cytotoxicity, enterotoxicity, and lethality in mice.Infect Immun. 2010 Apr;78(4):1772-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01051-09. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20086084 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Mouse Model of Enteric Vibrio parahaemolyticus Infection Reveals that the Type III Secretion System 2 Effector VopC Plays a Key Role in Tissue Invasion and Gastroenteritis.mBio. 2019 Dec 17;10(6):e02608-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02608-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31848276 Free PMC article.
-
[Type III secretion system of Vibrio parahaemolyticus--a review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009 Jul;49(7):848-52. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2009. PMID: 19873746 Review. Chinese.
-
Structural and regulatory mutations in Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems display variable effects on virulence.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2014 Dec;361(2):107-14. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12619. Epub 2014 Oct 31. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2014. PMID: 25288215 Free PMC article.
-
The role of type III secretion system 2 in Vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity.J Microbiol. 2012 Oct;50(5):719-25. doi: 10.1007/s12275-012-2550-2. Epub 2012 Nov 4. J Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23124738 Review.
Cited by
-
Vibrio type III effector VPA1380 is related to the cysteine protease domain of large bacterial toxins.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 6;9(8):e104387. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104387. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25099122 Free PMC article.
-
ArcB initiates quorum sensing to regulate T3SS in Vibrio alginolyticus by recognizing bacterial and host-derived autoinducer-2 as a kinase.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 May 28;23(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02258-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40437596 Free PMC article.
-
The Vibrio parahaemolyticus ToxRS regulator is required for stress tolerance and colonization in a novel orogastric streptomycin-induced adult murine model.Infect Immun. 2012 May;80(5):1834-45. doi: 10.1128/IAI.06284-11. Epub 2012 Mar 5. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22392925 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Vibrio parahaemolyticus in type III secretion system 1 inducing conditions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014 Jan 20;4:1. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00001. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24478989 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Screens Reveal Requirements for Host Cell Sulfation and Fucosylation in Bacterial Type III Secretion System-Mediated Cytotoxicity.Cell Host Microbe. 2016 Aug 10;20(2):226-37. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2016.06.010. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Cell Host Microbe. 2016. PMID: 27453484 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

