The chemokine receptor CXCR2 ligand KC (CXCL1) mediates neutrophil recruitment and is critical for development of experimental Lyme arthritis and carditis
- PMID: 20823213
- PMCID: PMC2976349
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00798-10
The chemokine receptor CXCR2 ligand KC (CXCL1) mediates neutrophil recruitment and is critical for development of experimental Lyme arthritis and carditis
Abstract
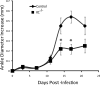
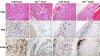
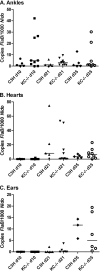
Deletion of the chemokine receptor CXCR2 prevents the recruitment of neutrophils into tissues and subsequent development of experimental Lyme arthritis. Following footpad inoculation of Borrelia burgdorferi, the agent of Lyme disease, expression of the CXCR2 ligand KC (CXCL1) is highly upregulated in the joints of arthritis-susceptible mice and is likely to play an important role in the recruitment of neutrophils to the site of infection. To test this hypothesis, we infected C3H KC(-/-) mice with B. burgdorferi and followed the development of arthritis and carditis. Ankle swelling was significantly attenuated during the peak of arthritis in the KC(-/-) mice. Arthritis severity scores were significantly lower in the KC(-/-) mice on days 11 and 21 postinfection, with fewer neutrophils present in the inflammatory lesions. Cardiac lesions were also significantly decreased in KC(-/-) mice at day 21 postinfection. There were, however, no differences between C3H wild-type and KC(-/-) mice in spirochete clearance from tissues. Two other CXCR2 ligands, LIX (CXCL5) and MIP-2 (CXCL2), were not increased to compensate for the loss of KC, and the production of several innate cytokines was unaltered. These results demonstrate that KC plays a critical nonredundant role in the development of experimental Lyme arthritis and carditis via CXCR2-mediated recruitment of neutrophils into the site of infection.
Figures
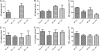
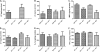
References
-
- Anguita, J., S. W. Barthold, S. Samanta, J. Ryan, and E. Fikrig. 1999. Selective anti-inflammatory action of interleukin-11 in murine Lyme disease: arthritis decreases while carditis persists. J. Infect. Dis. 179:734-737. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, A. L., S. W. Barthold, D. H. Persing, and D. S. Beck. 1992. Carditis in Lyme disease susceptible and resistant strains of laboratory mice infected with Borrelia burgdorferi. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 47:249-258. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, D. A., J. A. Major, A. Chudyk, and T. A. Hamilton. 2004. Neutrophil chemoattractant genes KC and MIP-2 are expressed in different cell populations at sites of surgical injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 75:641-648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

