Oral methylphenidate normalizes cingulate activity in cocaine addiction during a salient cognitive task
- PMID: 20823246
- PMCID: PMC2944718
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1011455107
Oral methylphenidate normalizes cingulate activity in cocaine addiction during a salient cognitive task
Abstract
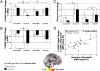
Anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) hypoactivations during cognitive demand are a hallmark deficit in drug addiction. Methylphenidate (MPH) normalizes cortical function, enhancing task salience and improving associated cognitive abilities, in other frontal lobe pathologies; however, in clinical trials, MPH did not improve treatment outcome in cocaine addiction. We hypothesized that oral MPH will attenuate ACC hypoactivations and improve associated performance during a salient cognitive task in individuals with cocaine-use disorders (CUD). In the current functional MRI study, we used a rewarded drug cue-reactivity task previously shown to be associated with hypoactivations in both major ACC subdivisions (implicated in default brain function) in CUD compared with healthy controls. The task was performed by 13 CUD and 14 matched healthy controls on 2 d: after ingesting a single dose of oral MPH (20 mg) or placebo (lactose) in a counterbalanced fashion. Results show that oral MPH increased responses to this salient cognitive task in both major ACC subdivisions (including the caudal-dorsal ACC and rostroventromedial ACC extending to the medial orbitofrontal cortex) in the CUD. These functional MRI results were associated with reduced errors of commission (a common impulsivity measure) and improved task accuracy, especially during the drug (vs. neutral) cue-reactivity condition in all subjects. The clinical application of such MPH-induced brain-behavior enhancements remains to be tested.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.Z.G. received a consultation fee from Medical Directions, Inc., for design of educational material and an honoraria fee from the Federal Judicial Center and the Gruter Institute for Law and Behavioral Research for lectures, both about neuroimaging in drug addiction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Anterior cingulate cortex hypoactivations to an emotionally salient task in cocaine addiction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jun 9;106(23):9453-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900491106. Epub 2009 May 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19478067 Free PMC article.
-
Oral methylphenidate normalizes cingulate activity and decreases impulsivity in cocaine addiction during an emotionally salient cognitive task.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 Jan;36(1):366-7. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.145. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21116260 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Role of the anterior cingulate and medial orbitofrontal cortex in processing drug cues in cocaine addiction.Neuroscience. 2007 Feb 23;144(4):1153-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.11.024. Epub 2006 Dec 29. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17197102 Free PMC article.
-
A critical review of the literature on attentional bias in cocaine use disorder and suggestions for future research.Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014 Dec;22(6):469-83. doi: 10.1037/a0037806. Epub 2014 Sep 15. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25222545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methylphenidate Treatment of Cognitive Dysfunction in Adults After Mild to Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury: Rationale, Efficacy, and Neural Mechanisms.Front Neurol. 2019 Sep 12;10:925. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00925. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31572283 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Finding the self by losing the self: Neural correlates of ego-dissolution under psilocybin.Hum Brain Mapp. 2015 Aug;36(8):3137-53. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22833. Epub 2015 May 22. Hum Brain Mapp. 2015. PMID: 26010878 Free PMC article.
-
Neurochemical enhancement of conscious error awareness.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 22;32(8):2619-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4052-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22357846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of chronic cocaine self-administration on cognition and cerebral glucose utilization in Rhesus monkeys.Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Nov 15;72(10):856-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 Jun 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22672928 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced metabolism in brain "control networks" following cocaine-cues exposure in female cocaine abusers.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 23;6(2):e16573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016573. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21373180 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
N-Acetylcysteine reduces cocaine-cue attentional bias and differentially alters cocaine self-administration based on dosing order.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017 Sep 1;178:452-460. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.05.039. Epub 2017 Jun 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017. PMID: 28711811 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

