High-speed crystal detection and characterization using a fast-readout detector
- PMID: 20823554
- PMCID: PMC6691516
- DOI: 10.1107/S0907444910028192
High-speed crystal detection and characterization using a fast-readout detector
Abstract
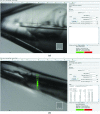
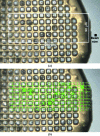
A novel raster-scanning method combining continuous sample translation with the fast readout of a Pilatus P6M detector has been developed on microfocus beamline I24 at Diamond Light Source. This fast grid-scan tool allows the rapid evaluation of large sample volumes without the need to increase the beam size at the sample through changes in beamline hardware. A slow version is available for slow-readout detectors. Examples of grid-scan use in centring optically invisible samples and in detecting and characterizing numerous microcrystals on a mesh-like holder illustrate the most common applications of the grid scan now in routine use on I24.
Figures
References
-
- Beteva, A. et al. (2006). Acta Cryst. D62, 1162–1169. - PubMed
-
- Caffrey, M. (2000). Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 10, 486–497. - PubMed
-
- Evans, G., Alianelli, L., Burt, M., Wagner, A. & Sawhney, K. (2006). AIP Conf. Proc. 879, 836–839.
-
- Hülsen, G., Broennimann, C., Eikenberry, E. F. & Wagner, A. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 550–557.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

