Linking power Doppler ultrasound to the presence of th17 cells in the rheumatoid arthritis joint
- PMID: 20824142
- PMCID: PMC2931706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012516
Linking power Doppler ultrasound to the presence of th17 cells in the rheumatoid arthritis joint
Abstract
Background: Power Doppler ultrasound (PDUS) is increasingly used to assess synovitis in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Prior studies have shown correlations between PDUS scores and vessel counts, but relationships with T cell immunopathology have not been described.
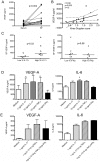
Methodology/principal findings: PBMC were isolated from healthy controls (HC) or RA patients and stimulated ex vivo with PMA and ionomycin for 3 hours in the presence of Golgistop. Paired synovial fluid (SF) or synovial tissue (ST) were analysed where available. Intracellular expression of IL-17, IFNgamma, and TNFalpha by CD4+ T cells was determined by flow cytometry. Synovial blood flow was evaluated by PDUS signal at the knees, wrists and metacarpophalangeal joints of RA patients. Serum, SF and fibroblast culture supernatant levels of vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) were measured by ELISA. The frequency of IL17+IFNgamma-CD4+ T cells (Th17 cells) was significantly elevated in peripheral blood (PB) from RA patients vs. HC (median (IQR) 0.5 (0.28-1.59)% vs. 0.32 (0.21-0.54)%, p = 0.005). Th17 cells were further enriched (mean 6.6-fold increase) in RA SF relative to RA PB. Patients with active disease had a higher percentage of IL-17+ T cells in ST than patients in remission, suggesting a possible role for Th17 cells in active synovitis in RA. Indeed, the percentage of Th17 cells, but not Th1, in SF positively correlated with CRP (r = 0.51, p = 0.04) and local PDUS-defined synovitis (r = 0.61, p = 0.002). Furthermore, patients with high levels of IL-17+CD4+ T cells in SF had increased levels of the angiogenic factor VEGF-A in SF. Finally, IL-17, but not IFNgamma, increased VEGF-A production by RA synovial fibroblasts in vitro.
Conclusions/significance: Our data demonstrate a link between the presence of pro-inflammatory Th17 cells in SF and local PDUS scores, and offer a novel immunological explanation for the observation that rapid joint damage progression occurs in patients with persistent positive PDUS signal.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Interleukin-17+CD8+ T cells are enriched in the joints of patients with psoriatic arthritis and correlate with disease activity and joint damage progression.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 May;66(5):1272-81. doi: 10.1002/art.38376. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 24470327 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Th1 and Th2 cytokines expressing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis by flow cytometry.J Rheumatol. 2000 May;27(5):1128-35. J Rheumatol. 2000. PMID: 10813277
-
Greyscale and power Doppler ultrasonographic evaluation of normal synovial joints: correlation with pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and angiogenic factors.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015 Mar;54(3):458-62. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keu354. Epub 2014 Sep 5. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 25193808
-
[The role of T helper 17 cells of synovial fluid in rheumatoid arthritis].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Nov;44(6):907-10. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 24490499 Chinese.
-
Effector Functions of CD4+ T Cells at the Site of Local Autoimmune Inflammation-Lessons From Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 12;10:353. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00353. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30915067 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mast cells are the main interleukin 17-positive cells in anticitrullinated protein antibody-positive and -negative rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis synovium.Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(5):R150. doi: 10.1186/ar3466. Epub 2011 Sep 20. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011. Retraction in: Arthritis Res Ther. 2015 Dec 09;17:354. doi: 10.1186/s13075-015-0847-3. PMID: 21933391 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Quantitative imaging by pixel-based contrast-enhanced ultrasound reveals a linear relationship between synovial vascular perfusion and the recruitment of pathogenic IL-17A-F+IL-23+ CD161+ CD4+ T helper cells in psoriatic arthritis joints.Clin Rheumatol. 2017 Feb;36(2):391-399. doi: 10.1007/s10067-016-3500-x. Epub 2016 Dec 20. Clin Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 27995384
-
Cartilage and bone damage in rheumatoid arthritis.Reumatologia. 2018;56(2):111-120. doi: 10.5114/reum.2018.75523. Epub 2018 May 9. Reumatologia. 2018. PMID: 29853727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in synovial pathotypes of rheumatoid arthritis: an exploratory study.Eur Radiol. 2025 Aug 20. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11921-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40836017
-
Enhanced and persistent levels of interleukin (IL)-17⁺ CD4⁺ T cells and serum IL-17 in patients with early inflammatory arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2013 Nov;174(2):292-301. doi: 10.1111/cei.12167. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23815507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–422. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Fossiez F, Taupin JL, Miossec P. Enhancing effect of IL-17 on IL-1-induced IL-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor production by rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes and its regulation by Th2 cytokines. J Immunol. 1998;161:409–414. - PubMed
-
- Chabaud M, Garnero P, Dayer JM, Guerne PA, Fossiez F, et al. Contribution of interleukin 17 to synovium matrix destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine. 2000;12:1092–1099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

