The metamorphosis of heterometallic trinuclear antiferromagnetic complexes into nano-sized superparamagnetic spinels
- PMID: 20824196
- PMCID: PMC2930828
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.12.040
The metamorphosis of heterometallic trinuclear antiferromagnetic complexes into nano-sized superparamagnetic spinels
Abstract
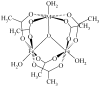
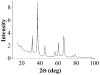
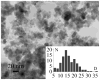
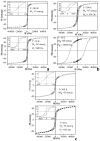
Thermal decomposition of the trinuclear heterometallic oxoacetates [Fe(2)M(μ(3)-O)(CH(3)COO)(6)(H(2)O)(3)] has been used as a single-precursor method for synthesis of the spinel-structured ternary oxides MFe(2)O(4) (M = Mn(II), Co(II), and Ni(II)). This facile process occurring at 320 °C results in the formation of nanocrystalline, (7-20 nm) highly pure stoichiometric ferrites in quantitative yield. The magnetic properties of these nanoparticulate ferrites were studied in the 10-300 K temperature range, revealing superparamagnetic behaviour for the Ni and Mn particles and ferromagnetic behavior for the Co ones at room temperature. Their blocking temperatures follow the order: CoFe(2)O(4) > MnFe(2)O(4) > NiFe(2)O(4).
Figures

References
-
- Kodama HRH, Berkowitz AE, McNiff EJJ, Foner S. J Appl Phys. 1997;81:5552.
-
- Muroi M, Street R, McCormick PG. Phys Rev B. 2001;63:184414.
-
- O’Brien S, Brus L, Murray CB. J Am Chem Soc. 2001;123:12085. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Chen Q, Hou B, Peng Z. Eur J Inorg Chem. 2004:1165.
-
- Li F, Liu J, Evans D, Duan X. Chem Mater. 2004;16:1597.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
