Acamprosate for alcohol dependence
- PMID: 20824837
- PMCID: PMC12147086
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004332.pub2
Acamprosate for alcohol dependence
Abstract
Background: Alcohol dependence is among the main leading health risk factors in most developed and developing countries. Therapeutic success of psychosocial programs for relapse prevention is moderate, but could potentially be increased by an adjuvant treatment with the glutamate antagonist acamprosate.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and tolerability of acamprosate in comparison to placebo and other pharmacological agents.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Drugs and Alcohol Group (CDAG) Specialized Register, PubMed, EMBASE and CINAHL in January 2009 and inquired manufacturers and researchers for unpublished trials.
Selection criteria: All double-blind randomised controlled trials (RCTs) which compare the effects of acamprosate with placebo or active control on drinking-related outcomes.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data. Trial quality was assessed by one author and cross-checked by a second author. Individual patient data (IPD) meta-analyses were used to verify the primary effectiveness outcomes.
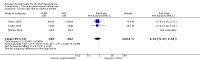
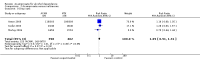
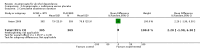
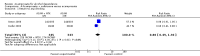
Main results: 24 RCTs with 6915 participants fulfilled the criteria of inclusion and were included in the review. Compared to placebo, acamprosate was shown to significantly reduce the risk of any drinking RR 0.86 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.91); NNT 9.09 (95% CI 6.66 to 14.28) and to significantly increase the cumulative abstinence duration MD 10.94 (95% CI 5.08 to 16.81), while secondary outcomes (gamma-glutamyltransferase, heavy drinking) did not reach statistical significance. Diarrhea was the only side effect that was more frequently reported under acamprosate than placebo RD 0.11 (95% 0.09 to 0.13); NNTB 9.09 (95% CI 7.69 to 11.11). Effects of industry-sponsored trials RR 0.88 (95% 0.80 to 0.97) did not significantly differ from those of non-profit funded trials RR 0.88 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.96). In addition, the linear regression test did not indicate a significant risk of publication bias (p = 0.861).
Authors' conclusions: Acamprosate appears to be an effective and safe treatment strategy for supporting continuous abstinence after detoxification in alcohol dependent patients. Even though the sizes of treatment effects appear to be rather moderate in their magnitude, they should be valued against the background of the relapsing nature of alcoholism and the limited therapeutic options currently available for its treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
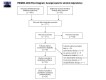
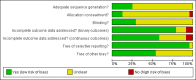

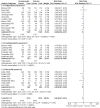

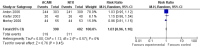
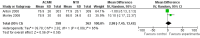
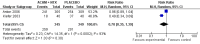
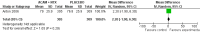
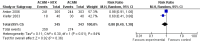
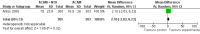
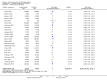












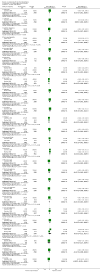

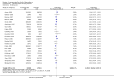




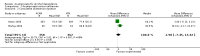




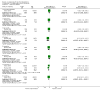










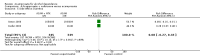



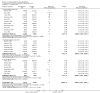
Comment in
-
ACP Journal Club. Review: Acamprosate increases abstinence in patients with alcohol dependence.Ann Intern Med. 2011 Jan 18;154(2):JC1-10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-2-201101180-02010. Ann Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21242352 No abstract available.
-
Acamprosate reduces risk of return to drinking after detoxification, but is similarly effective to naltrexone.Evid Based Ment Health. 2011 Feb;14(1):22. doi: 10.1136/ebmh.14.1.22. Evid Based Ment Health. 2011. PMID: 21266619 No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Anton 2006 {published data only}
-
- Anton RF, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Cisler RA, Couper D, Donovan DM, et al. Combined pharmacotherapies and behavioral interventions for alcohol dependence: the COMBINE study: a randomised controlled trial. JAMA 2006;295:2003‐17. - PubMed
Baltieri 2003 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Baltieri D A, Andrade A G. Acamprosate in alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled efficacy study in a standard clinical setting. Journal of studies on alcohol 2004;65:136‐9. - PubMed
Barrias 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Barrias JA, Chabac S, Ferreira L, Fonte A, Potgieter AS, Teixeira de Sousa E. Acamprosate: multicenter Portuguese efficacy and tolerance evaluation study. Psiquiatria Clinica 1997;18:149‐60.
Besson 1998 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Besson J, Aeby F, Kasas A, Lehert P, Potgieter A. Combined efficacy of acamprosate and disulfiram in the treatment of alcoholism: a controlled study. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 1998;22:573‐9. - PubMed
Borg 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Borg S. Randomized controlled trial of acamprosate versus placebo in Swedish alcoholics. Unpublished trial. Data on file Lipha SA, Lyon, 2003.
Chick 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Chick J, Howlett H, Morgan M Y, Ritson B. United Kingdom Multicentre Acamprosate Study (UKMAS): a 6‐month prospective study of acamprosate versus placebo in preventing relapse after withdrawal from alcohol. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2000;35:176‐87. - PubMed
Geerlings 1997 {published data only}
-
- Geerlings PJ, Ansoms C, Brink W. Acamprosate and prevention of relapse in alcoholics. Results of a randomised, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study in out‐patient alcoholics in The Netherlands, Belgium and Luxembourg. European Addiction Research 1997;3:129‐37.
Gual 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gual A, Lehert P. Acamprosate during and after acute alcohol withdrawal: a double‐blind placebo‐controlled study in Spain. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2001;36:413‐8. - PubMed
Kiefer 2003 {published data only}
-
- Kiefer F, Jahn H, Tarnaske T, Helwig H, Briken P, Holzbach R, et al. Comparing and combining naltrexone and acamprosate in relapse prevention of alcoholism: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Archives of General Psychiatry 2003;60:92‐9. - PubMed
Ladewig 1993 {published data only}
-
- Ladewig D, Knecht T, Leher P, Fendl A. Acamprosate‐‐a stabilizing factor in long‐term withdrawal of alcoholic patients. Therapeutische Umschau 1993;50:182‐8. - PubMed
Lhuintre 1985 {published data only}
-
- Lhuintre J P, Daoust M, Moore ND, Chretien P, Saligaut C, Tran G, et al. Ability of calcium bis acetyl homotaurine, a GABA agonist, to prevent relapse in weaned alcoholics. Lancet 1985;1:1014‐6. - PubMed
Lhuintre 1990 {published data only}
-
- Lhuintre JP, Moore N, Tran G, Steru L, Langrenon S, Daoust M, et al. Acamprosate appears to decrease alcohol intake in weaned alcoholics. Alcohol and Alcoholism 1990;25:613‐22. - PubMed
Mason 2006 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Mason BJ, Goodman AM, Chabac S, Lehert P. Effect of oral acamprosate on abstinence in patients with alcohol dependence in a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial: the role of patient motivation. Journal of Psychiatric Research 2006;40:383‐93. - PubMed
Morley 2006 {published data only}
-
- Morley KC, Teesson M, Reid SC, Sannibale C, Thomson C, Phung N, et al. Naltrexone versus acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: A multi‐centre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Addiction 2006;101:1451‐62. - PubMed
Namkoong 2003 {published data only}
-
- Namkoong K, Lee BO, Lee PG, Choi MJ, Lee E. Acamprosate in Korean alcohol‐dependent patients: a multi‐centre, randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2003;38:135‐41. - PubMed
Niederhofer 2002 {published data only}
-
- Niederhofer H, Staffen W. Acamprosate and its efficacy in treating alcohol dependent adolescents. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 2003;12:144‐8. - PubMed
Paille 1995 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Paille FM, Guelfi JD, Perkins AC, Royer RJ, Steru L, Parot P. Double‐blind randomised multi centre trial of acamprosate in maintaining abstinence from alcohol. Alcohol and Alcoholism 1995;30:239‐47. - PubMed
Pelc 1992 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pelc I Le Bon O Lehert P Verbanck P. Acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: A six month post detoxification study. In: Naranjo C, Sellers E editor(s). Novel pharmacological interventions for alcoholism. New York: Springer, 1992:348‐52.
Pelc 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Pelc I, Verbanck P, Bon O, Gavrilovic M, Lion K, Lehert P. Efficacy and safety of acamprosate in the treatment of detoxified alcohol‐dependent patients. A 90‐day placebo‐controlled dose‐finding study. British Journal of Psychiatry 1997;171:73‐7. - PubMed
Poldrugo 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Poldrugo F. Acamprosate treatment in a long‐term community‐based alcohol rehabilitation programme. Addiction 1997;92:1537‐46. - PubMed
Rousseaux 1996 {published data only}
-
- Roussaux JP, Hers D, Ferauge M. Does acamprosate diminish the appetite for alcohol in weaned alcoholics?. Journal de Pharmacie de Belgique 1996;51:65‐8. - PubMed
Sass 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Sass H, Soyka M, Mann K, Zieglgansberger W. Relapse prevention by acamprosate. Results from a placebo‐controlled study on alcohol dependence. Archives of General Psychiatry 1996;53:673‐80. - PubMed
Tempesta 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tempesta E, Janiri L, Bignamini A, Chabac S, Potgieter A. Acamprosate and relapse prevention in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a placebo‐controlled study. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2000;35:202‐9. - PubMed
Whitworth 1996 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Whitworth AB, Fischer F, Lesch OM, Nimmerrichter A, Oberbauer H, Platz T, et al. Comparison of acamprosate and placebo in long‐term treatment of alcohol dependence. Lancet 1996;347:1438‐42. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Boeijinga 2004 {published data only}
-
- Boeijinga PH, Parot P, Soufflet L, Landron F, Danel T, Gendre I, et al. Pharmacodynamic effects of acamprosate on markers of cerebral function in alcohol‐dependent subjects administered as pretreatment and during alcohol abstinence. Neuropsychobiology 2004;50(1):71‐7. - PubMed
Buri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Buri C, Moggi F, Giovanoli A, Strik W. Prescription procedures in medication for relapse prevention after inpatient treatment for alcohol use disorders in Switzerland. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2007;42(4):333‐9. - PubMed
Croissant 2006 {published data only}
-
- Croissant B, Diehl A, Klein O, Zambrano S, Nakovics H, Heinz A, et al. A pilot study of oxcarbazepine versus acamprosate in alcohol‐dependent patients. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2006;30(4):630‐5. - PubMed
de Sousa 2005 {published data only}
-
- Sousa A. An open randomised study comparing disulfiram and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2005;40(6):545‐8. - PubMed
De Wildt 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wildt WA, Schippers GM, Brink W, Potgieter A S, Deckers F, Bets D. Does psychosocial treatment enhance the efficacy of acamprosate in patients with alcohol problems?. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2002;37(4):375‐82. - PubMed
Feeney 2002 {published data only}
-
- Feeney GF, Young RM, Connor JP, Tucker J, McPherson A. Cognitive behavioural therapy combined with the relapse‐prevention medication acamprosate: are short‐term treatment outcomes for alcohol dependence improved?. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry 2002;36(5):622‐8. - PubMed
Florez 2008 {published data only}
-
- Florez G, Garcia‐Portilla P, Alvarez S, Saiz P A, Nogueiras L, Bobes J. Using topiramate or naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol‐dependent patients. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32(7):1251‐9. - PubMed
Fuchs 2002 {published data only}
-
- Fuchs WJ, Riebenfeld D. Acamprosate and psychosocial intervention. An integrative treatment approach for prevention of alcohol dependent patients in Switzerland. Praxis (Bern 1994) 2002;91(17):735‐42. - PubMed
Gerra 1992 {published data only}
-
- Gerra G, Caccavari R, Delsignore R. Effects of fluoxetine and Ca‐acetyl‐homotaurinate on alcohol intake in familial and nonfamilial. Current Therapeutic Research 1992;52:291‐5.
Hammarberg 2004 {published data only}
-
- Hammarberg A, Wennberg P, Beck O, Franck J. A comparison of two intensities of psychosocial intervention for alcohol dependent patients treated with acamprosate. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2004;39(3):251‐5. - PubMed
Han 2008 {published data only}
-
- Han DH, Lyool I K, Sung YH, Lee SH, Renshaw PF. The effect of acamprosate on alcohol and food craving in patients with alcohol dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2008;93(3):279‐83. - PubMed
Johnson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Johnson BA, O'Malley SS, Ciraulo DA, Roache JD, Chambers RA, Sarid‐Segal O, et al. Dose‐ranging kinetics and behavioral pharmacology of naltrexone and acamprosate, both alone and combined, in alcohol‐dependent subjects. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacoly 2003;23(3):281‐93. - PubMed
Kampman 2009 {published data only}
Kiritze‐Topor 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kiritze‐Topor P, Huas D, Rosenzweig C, Comte S, Paille F, Lehert P. A pragmatic trial of acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence in primary care. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2004;39(6):520‐7. - PubMed
Laaksonen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Laaksonen E, Koski‐Jannes A, Salaspuro M, Ahtinen H, Alho H. A randomised, multi centre, open‐label, comparative trial of disulfiram, naltrexone and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2008;43(1):53‐61. - PubMed
Mason 2002 {published data only}
-
- Mason BJ, Goodman AM, Dixon RM, Hameed MH, Hulot T, Wesnes K, et al. A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interaction study of acamprosate and naltrexone. Neuropsychopharmacology 2002;27(4):596‐606. - PubMed
Nespor 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nespor K, Csemy L. Treatment and prevention of alcohol‐related problems and evidence based medicine. Casopis Lekaru Ceskych 2006;145(12):964‐5. - PubMed
Ooteman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Ooteman W, Koeter MW, Verheul R, Schippers GM, Brink W. The effect of naltrexone and acamprosate on cue‐induced craving, autonomic nervous system and neuroendocrine reactions to alcohol‐related cues in alcoholics. European Neuropsychopharmacoly 2007;17(8):558‐66. - PubMed
Pelc 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pelc I, Ansoms C, Lehert P, Fischer F, Fuchs W J, Landron F, et al. The European NEAT program: an integrated approach using acamprosate and psychosocial support for the prevention of relapse in alcohol‐dependent patients with a statistical modelling of therapy success prediction. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research 2002;26(10):1529‐38. - PubMed
Reid 2005 {published data only}
-
- Reid SC, Teesson M, Sannibale C, Matsuda M, Haber PS. The efficacy of compliance therapy in pharmacotherapy for alcohol dependence: a randomised controlled trial. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 2005;66(6):833‐41. - PubMed
Rubio 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rubio G, Jimenez‐Arriero MA, Ponce G, Palomo T. Naltrexone versus acamprosate: one year follow‐up of alcohol dependence treatment. Alcohol and Alcoholism 2001;36(5):419‐25. - PubMed
Rychlik 2001 {published data only}
-
- Rychlik R, Paschen B, Kirchhoff D, Daniel D, Pfeil T, Kilburg A. Adjuvant drug treatment of alcoholism with acamprosate: between sectorial budgets and disease management. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 2001;126(33):899‐904. - PubMed
Soyka 2002 {published data only}
-
- Soyka M, Preuss U, Schuetz C. Use of acamprosate and different kinds of psychosocial support in relapse prevention of alcoholism. Results from a non‐blind, multicentre study. Drugs in Road Traffic 2002;3(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Staner 2006 {published data only}
-
- Staner L, Boeijinga P, Danel T, Gendre I, Muzet M, Landron F, et al. Effects of acamprosate on sleep during alcohol withdrawal: A double‐blind placebo‐controlled polysomnographic study in alcohol‐dependent subjects. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2006;30(9):1492‐9. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Gaebel {unpublished data only}
-
- Integrative Therapy in Alcoholism. Ongoing study May 2003.
Garbutt {published data only}
-
- Study of Acamprosate for Alcohol Dependence in a Family Medicine Clinic. Ongoing study August 2006.
Haber {unpublished data only}
-
- Trial for the Treatment of Alcohol Dependence. Ongoing study March 2003.
Mann {published data only}
-
- Individually Adapted Therapy of Alcoholism. Ongoing study November 2002.
Petrakis {published data only}
-
- Treatment With Acamprosate in Patients With Schizophrenia and Comorbid Alcoholism. Ongoing study September 2006.
Pettinati {published data only}
-
- Acamprosate Initiated During Alcohol Detoxification. Ongoing study October 2006.
Sonne {published data only}
-
- Acamprosate in Alcoholics With Comorbid Anxiety or Depression. Ongoing study April 2006.
Witte {published data only}
-
- Acamprosate Added to Escitalopram and Behavioral Treatment for Comorbid Depression and Alcoholism. Ongoing study March 2007.
Additional references
Adams 2007
Alonso 2004
-
- Alonso J, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, Bruffaerts R, Brugha TS, Bryson H. Prevalence of mental disorders in Europe: results from the European Study of the Epidemiology of Mental Disorders (ESEMeD) project. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavia Supplement 2004;420:21‐7. - PubMed
Arroll 2009
Bachteler 2005
-
- Bachteler D, Economidou D, Danysz W, Ciccocioppo R, Spanagel R. The effects of acamprosate and neramexane on cue‐induced reinstatement of ethanol‐seeking behavior in rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005;30(6):1104‐10. - PubMed
Berglund 2003
-
- Berglund MA, Franck J, Fridell M, Hakanson I, Johansson BA. Treatment of alcohol and drug abuse ‐ an evidence‐based review. Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care (SBU) 2003; Vol. 156, issue 1.
Bouza 2004
-
- Bouza C, Angeles M, Munoz A, Amate JM. Efficacy and safety of naltrexone and acamprosate in the treatment of alcohol dependence: a systematic review. Addiction 2004;99(7):811‐28. - PubMed
Brockwell 2001
-
- Brockwell SE, Gordon IR. A comparison of statistical methods for meta‐analysis. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(6):825‐40. - PubMed
Cano‐Cebrian 2003
-
- Cano‐Cebrian MJ, Zornoza‐Sabina T, Guerri C, Polache A, Granero L. Acamprosate blocks the increase in dopamine extracellular levels in nucleus accumbens evoked by chemical stimulation of the ventral hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology 2003;368(4):324‐7. - PubMed
Chan 2004
-
- Chan AW, Hrobjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomised trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291(20):2457‐65. - PubMed
Chick 2003
-
- Chick J, Lehert P, Landron F. Does acamprosate improve reduction of drinking as well as aiding abstinence?. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2003;17(4):397‐402. - PubMed
Citrome 2008
-
- Citrome L. Compelling or irrelevant? Using number needed to treat can help decide. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavia 2008;117(6):412‐9. - PubMed
Cole 2000
-
- Cole JC, Littleton JM, Little HJ. Acamprosate, but not naltrexone, inhibits conditioned abstinence behaviour associated with repeated ethanol administration and exposure to a plus‐maze. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;147(4):403‐11. - PubMed
Czachowski 2001
-
- Czachowski CL, Legg BH, Samson HH. Effects of acamprosate on ethanol‐seeking and self‐administration in the rat. Alcoholism Clinical and Experimental Research 2001;25(3):344‐50. - PubMed
Deeks 2008
-
- Deeks J, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): Johm Wiley & Sons, 2008:243‐293.
DerSimonian 1986
-
- DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta‐analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 1986;7(3):177‐88. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Ferri 2006
Heyser 1998
-
- Heyser CJ, Schulteis G, Durbin P, Koob GF. Chronic acamprosate eliminates the alcohol deprivation effect while having limited effects on baseline responding for ethanol in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 1998;18(2):125‐33. - PubMed
Higgins 2001
-
- Higgins JP, Whitehead A, Turner RM, Omar RZ, Thompson SG. Meta‐analysis of continuous outcome data from individual patients. Statistics in Medicine 2001;20(15):2219‐41. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): Johm Wiley & Sons, 2008:243‐296.
Hopkins 2002
-
- Hopkins JS, Garbutt JC, Poole CL, West SL, Carey TS. Naltrexone and acamprosate: Meta‐analysis of two medical treatments for alcoholism. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2002;26(Suppl):130A.
Huwiler‐Muntener 2002
-
- Huwiler‐Muntener K, Juni P, Junker C, Egger M. Quality of reporting of randomised trials as a measure of methodologic quality. JAMA 2002;287(21):2801‐4. - PubMed
ICAP 2003
-
- ICAP International Center for Alcohol Policies. International Drinking Guidelines [(http://www.icap.org/)]. Report Nr. 14 2003.
ICH 1996
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation. Guideline for Good ClinicalPractice E6(R1).. (http://www.ich.org/LOB/media/MEDIA482.pdf) 1996; Vol. Jun [cited 2009 Jan 20].
Kadden 1992
-
- Kadden R, Carroll K, Donovan D, Cooney N, Monti P, Abrams D, Litt M, Hester R. Cognitive‐Behavioral Coping Skills Therapy Manual: A Clinical Research Guide fro Therapists Treating Individuals with Alcohol Abuse and Dependence. NIAAA Project MATCH Monograph Series. National Institute on Alcoholism and Alcohol Abuse. Vol. 3, Rockville: Matson ED, 1992.
Kaner 2007
Keller 1972
-
- Keller M. On the loss‐of‐control phenomenon in alcoholism. British Journal of Addiction 1972;67:153‐66. - PubMed
Kiefer 2004
-
- Kiefer F, Andersohn F, Otte C, Wolf K, Jahn H, Wiedemann K. Long‐term effects of pharmacotherapy on relapse prevention in alcohol dependence. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2004;16:233‐8. - PubMed
Konnopka 2007
-
- Konnopka A, König HH. Direct and indirect costs attributable to alcohol consumption in Germany. Pharmacoeconomics 2007;25(7):605‐18. - PubMed
Kranzler 2001
-
- Kranzler HR, Kirk J. Efficacy of naltrexone and acamprosate for alcoholism treatment: a meta‐analysis. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2001;25(9):1335‐41. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2008
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for Studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Chichester (UK): Johm Wiley & Sons, 2008:95‐150.
Lehert 1993
-
- Lehert P. Review and discussion of statistical analysis of controlled clinical trials in alcoholism. Alcohol and Alcoholism Supplement 1993;2:157‐63. - PubMed
LeMagnen 1987
-
- LeMagnen J, Tran G, Durlach J. Lack of effects of Ca‐acetyl homotaurinate on chronic and acute toxicities of ethanol in rats. Alcohol and Alcohilsm 1987;4(2):103‐8. - PubMed
Levine 1986
-
- Levine J, Schooler NR. SAFTEE: a technique for the systematic assessment of side effects in clinical trials. Psychopharmacol Bulletin 1986;22(2):343‐81. - PubMed
Light 1984
-
- Light RJ, Pillemer BD. The science of reviewing research. Cambridge (MA): Harvard University Press, 1984.
Lipha 2002
-
- Lipha Pharmaceuticals Inc. Clincial Background Materials for Psychopharmacologic Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting. NDA 21‐431 2002.
Littleton 1995
-
- Littleton J. Acamprosate in alcohol dependence: how does it work?. Addiction 1995;90(9):1179‐88. - PubMed
Littleton 2003
-
- Littleton J, Zieglgansberger W. Pharmacological mechanisms of naltrexone and acamprosate in the prevention of relapse in alcohol dependence. American Journal of Addiction 2003;12 Supplement 1:3‐11. - PubMed
Mann 2004
-
- Mann K, Lehert P, Morgan M Y. The efficacy of acamprosate in the maintenance of abstinence in alcohol‐dependent individuals: results of a meta‐analysis. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2004;28(1):51‐63. - PubMed
Mann 2008
-
- Mann K, Kiefer F, Spanagel R, Littleton J. Acamprosate: recent findings and future research directions. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 2008;32(7):1105‐10. - PubMed
Mantel 1959
-
- Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1959;22(4):719‐48. - PubMed
Marlatt 1985
-
- Marlatt GA, Gordon J. Relapse prevention. New York: Guilford Press, 1985.
McGeehan 2003
McQueen 2009
MIller 1994
-
- Miller WR, Zweben A, DiClemente CC, Rychtarik RG. Motivational Enhancement Therapy manual: A clinical research guide for therapists treating individuals with alcohol abuse and dependence. Rockville, MD: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, 1994.
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Jones A, Lepage L, CONSORT Group (Consolitdated Standards for Reporting of Trials). The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel‐group randomized trials. JAMA 2001;285(15):1992‐5. - PubMed
Moher 2009
Moncrieff 2004
Moos 2006
Naassila 1998
-
- Naassila M, Hammoumi S, Legrand E, Durbin P, Daoust M. Mechanism of action of acamprosate. Part I. Characterization of spermidine‐sensitive acamprosate binding site in rat brain. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 1998;22(4):802‐9. - PubMed
Newell 1992
-
- Newell DJ. Intention‐to‐treat analysis: implications for quantitative and qualitative research. International Journal of Epidemiology 1992;21(5):837‐41. - PubMed
Nickerson 1998
-
- Nickerson RS. Confirmation Bias: A Ubiquitous Phenomenon. Review of General Psychology 1998;2:175‐7.
Nowinski 1995
-
- Nowinski J, Baker S, Carroll, K. Twelve Step Facilitation Therapy manual. A clinical research guide for therapists treating individuals with alcohol abuse and dependence. Rockville, MD: Project MATCH Monograph Series Volume I. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, 1995.
Olive 2002
-
- Olive MF, Nannini MA, Ou CJ, Koenig HN, Hodge CW. Effects of acute acamprosate and homotaurine on ethanol intake and ethanol‐stimulated mesolimbic dopamine release. European Journal of Pharmacology 2002;437(1‐2):55‐61. - PubMed
Pettinati 2004
-
- Pettinati HM, Weiss RD, Miller WR, Donovan D, Ernst DB, Rounsaville BJ. Medical Management Treatment Manual. A Clinical Research Guide for MedicallyTrained Clinicians Providing Pharmacotherapy as Part of the Treatment for AlcoholDependence. Vol 2. Vol. 2, No (NIH) 04‐5289: COMBINE Monograph Series, 2004.
Pildal 2007
-
- Pildal J, Hrobjartsson A, Jorgensen K J, Hilden J, Altman D G, Gotzsche P C. Impact of allocation concealment on conclusions drawn from meta‐analyses of randomized trials. International Journal of Epidemiology 2007;36(4):847‐57. - PubMed
Pocock 1987
-
- Pocock S J, Hughes M D, Lee R J. Statistical problems in the reporting of clinical trials. A survey of three medical journals. New England Journal of Medicine 1987;317(7):426‐32. - PubMed
Project Match Research Group 1997
-
- Project Match Research Group. Matching alcoholism treatment to client heterogeneity: Project Match posttreatment drinking outcomes. Journal of Studies on Alcoholism 1997;58:7‐29. - PubMed
Rabkin 1992
-
- Rabkin J G, Markowitz J S, Ocepek‐Welikson K, Wager S S. General versus systematic inquiry about emergent clinical events with SAFTEE: implications for clinical research. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 1992;12(1):3‐10. - PubMed
Rehm 2009
-
- Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M, Teerawattananon Y, Patra J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol‐use disorders. Lancet 2009;373(9682):2223‐33. - PubMed
Riley 2007
-
- Riley RD, Simmonds MC, Look MP. Evidence synthesis combining individual patient data and aggregate data: a systematic review identified current practice and possible methods. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2007;60(5):431‐49. - PubMed
Rosner 2008
-
- Rösner S, Leucht S, Lehert P, Soyka M. Acamprosate supports abstinence, naltrexone prevents excessive drinking: evidence from a meta‐analysis with unreported outcomes. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2008;22(1):11‐23. - PubMed
Rucker 2008
Schoechlin 2000
-
- Schoechlin C, Engel RR. Meta‐analysis of pharmacotherapeutic trials. In: Zernig G, Saria A, Kurz M, O'Malley S editor(s). Handbook of Alcoholism. Innsbruck: Innsbruck University Press, 2000:339‐351.
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF. Subverting randomisation in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;274(18):1456‐8. - PubMed
Selzer 1971
-
- Selzer ML. The Michigan Alcoholism Screening Test (MAST): The quest for a new diagnostic instrument. American Journal of Psychiatry 1971;127:1653‐8. - PubMed
Skinner 1982
-
- Skinner HA, Allen BA. Alcohol dependence syndrome: measurement and validation. Journal of Abnormal Psychology 1982;91:199‐209. - PubMed
Skinner 1984
-
- Skinner HA, Horn JL. Alcohol Dependence Scale: Users Guide. Toronto: Addiction Research Foundation, 1984.
Slattery 2003
-
- Slattery J, Chick J. Prevention of Relapse in Alcohol Dependence. Health Technology Assesment Report 2003; Vol. 3.
Sobell 1988
-
- Sobell LC, Sobell MB, Riley DM, Schuller R, Pavan DS, Cancilla A, et al. The reliability of alcohol abusers' self‐reports of drinking and life events that occurred in the distant past. Journal of Studies on Alcohol 1988;49(3):225‐32. - PubMed
Sobell 1992
-
- Sobell LC, Toneatto T, Sobell MB, Leo GI, Johnson L. Alcohol abusers' perceptions of the accuracy of their self‐reports of drinking: implications for treatment. Addictive Behaviors 1992;17(5):507‐11. - PubMed
Spanagel 1996
-
- Spanagel R, Holter S M, Allingham K, Landgraf R, Zieglgansberger W. Acamprosate and alcohol: I. Effects on alcohol intake following alcohol deprivation in the rat. European Journal of Pharmacology 1996;305(1‐3):39‐44. - PubMed
Spanagel 1997
-
- Spanagel R, Zieglgansberger W. Anti‐craving compounds for ethanol: new pharmacological tools to study addictive processes. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 1997;18(2):54‐9. - PubMed
Spanagel 2003
-
- Spanagel R, Mann K. Acamprosate‐‐new preclinical research aspects. MMW, Fortschritte der Medizin 2003;145 Supplement(3):61‐4. - PubMed
Srisurapanont 2005
Tannock 1996
-
- Tannock I F. False‐positive results in clinical trials: multiple significance tests and the problem of unreported comparisons. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1996;88(3‐4):206‐7. - PubMed
The Nordic Cochrane Centre 2008 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre. Review Manager (RevMan). 5.0. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, 2008.
Turner 2000
-
- Turner R M, Omar R Z, Yang M, Goldstein H, Thompson S G. A multilevel model framework for meta‐analysis of clinical trials with binary outcomes. Statistics in Medicine 2000;19(24):3417‐32. - PubMed
Verheul 2005
-
- Verheul R, Lehert P, Geerlings P J, Koeter MW, Brink W. Predictors of acamprosate efficacy: results from a pooled analysis of seven European trials including 1485 alcohol‐dependent patients. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2005;178(2‐3):167‐73. - PubMed
WHO 2002
-
- WHO. The World Health Report: Reducing risk, promoting healthy life. The World Health Report. Geneva: WHO, 2002.
Williamson 2005
-
- Williamson PR, Gamble C, Altman DG, Hutton JL. Outcome selection bias in meta‐analysis. Statistical Methods in Medical Research 2005;14(5):515‐24. - PubMed
Wood 2008
Zeise 1993
-
- Zeise M L, Kasparov S, Capogna M, Zieglgansberger W. Acamprosate (calciumacetylhomotaurinate) decreases postsynaptic potentials in the rat neocortex: possible involvement of excitatory amino acid receptors. European Jorunal of Pharmacology 1993;231(1):47‐52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

