E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, E6-associated protein (E6-AP) regulates PI3K-Akt signaling and prostate cell growth
- PMID: 20826237
- PMCID: PMC3031754
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.08.011
E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, E6-associated protein (E6-AP) regulates PI3K-Akt signaling and prostate cell growth
Abstract
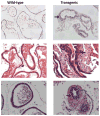
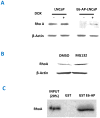
This study elucidates the role of E6-associated protein, E6-AP (a dual function steroid hormone receptor coactivator and ubiquitin-protein ligase) in the regulation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, prostate gland growth and proliferation. Here, we report the generation of transgenic mice and prostate cancer cell line, LNCaP cells that overexpress E6-AP protein. Using these models we show that the levels of total Akt and phosphorylated Akt (active Akt) are increased in E6-AP overexpressing prostate gland and LNCaP cells suggesting that E6-AP regulates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. The prostate glands in our transgenic mice are ~20% larger and produce preneoplastic lesions at the age of 18 months. Our data also suggest that E6-AP modulates PI3K-Akt signaling pathway by both androgen-independent and -dependent mechanisms. In the androgen-independent mechanism, E6-AP modulates PI3K-Akt signaling by regulating the protein levels of RhoA, a small GTPase, which is a negative regulator of the Akt signaling pathway. Further, we show that E6-AP, a known coactivator of AR, amplifies the androgen-dependent activation of PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. In addition, we show that stable overexpression of E6-AP in prostate cancer cells results in increased cell size and proliferation. Overall our data suggests that E6-AP regulates both the positive and negative modulators of the PI3K-Akt pathway in prostate cells which results in increased prostate cell growth, proliferation and decreased apoptosis.This article is part of a Special Issue entitled The 26S Proteasome: When degradation is just not enough!
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Khan OY, Fu G, Ismail A, Srinivasan S, Cao X, Tu Y, Lu S, Nawaz Z. Multifunction steroid receptor coactivator, E6-associated protein, is involved in development of the prostate gland. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:544–559. - PubMed
-
- Scheffner M, Huibregtse JM, Vierstra RD, Howley PM. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell. 1993;75:495–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

