Tribological properties of Ti-based alloys in a simulated bone-implant interface with Ringer's solution at fretting contacts
- PMID: 20826360
- PMCID: PMC2962574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2010.06.006
Tribological properties of Ti-based alloys in a simulated bone-implant interface with Ringer's solution at fretting contacts
Abstract
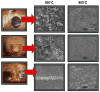
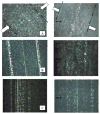
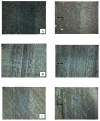
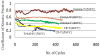
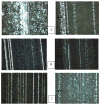
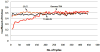
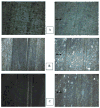
The wear properties of oxidized and non-oxidized gamma-TiAl (a potential biomaterial) as well as Ti-6Al-4V and CP-Ti disks were studied and characterized by means of standard wear tests using a custom made bone pin arrangement. The Ti-based disks were oxidized in air at 500 and 800 degrees C for one hour. The tribological properties of the oxides formed over the disks were studied using a linear reciprocating wear testing machine under both dry and simulated biological conditions using Ringer's solution. Loss of metal oxide and coefficient of friction values were determined from wear testing. From the results, abrasion and adhesion were the primary wear mechanisms in each of the three alloy-bone pairs. Specifically, the oxide formed on gamma-TiAl possessed the highest COF and wear resistance of the three materials which were studied. Also, as expected, bone wears down faster than the Ti-based metal oxide.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Böhler M, Kanz F, Schwarz B, Steffan I, Walter A, Plenk H, Knahr K. Adverse tissue reactions to wear particles from Co-alloy articulations, increased by alumina-blasting particle contamination from cementless Ti-based total hip implants. J Bone and Joint Surgery Br. 2002;84:128–136. - PubMed
-
- Choubey A, Basu B, Balasubramaniam R. Tribological behavior of Ti-based alloys in simulated body fluid solution at fretting contacts. Mater Sci Eng, A. 2004;379:234–239.
-
- Chu P, Liu X. Biomaterial Fabrication and Processing Handbook. New York: Taylor & Francis; 2008.
-
- Diebold U. The surface science of titanium dioxide. Surface Science Reports. 2003;48:53–229.
-
- Harman MK, Banks SA, Hodge WA. Wear analysis of a retrieved hip implant with titanium nitride coating. J Arthroplasty. 1997;12:938–945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

