Fluidity of HIV-1-specific T-cell responses during acute and early subtype C HIV-1 infection and associations with early disease progression
- PMID: 20826686
- PMCID: PMC2977870
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01472-10
Fluidity of HIV-1-specific T-cell responses during acute and early subtype C HIV-1 infection and associations with early disease progression
Abstract
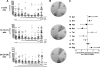
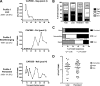
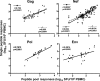
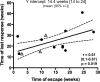
Deciphering immune events during early stages of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection is critical for understanding the course of disease. We characterized the hierarchy of HIV-1-specific T-cell gamma interferon (IFN-γ) enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay responses during acute subtype C infection in 53 individuals and associated temporal patterns of responses with disease progression in the first 12 months. There was a diverse pattern of T-cell recognition across the proteome, with the recognition of Nef being immunodominant as early as 3 weeks postinfection. Over the first 6 months, we found that there was a 23% chance of an increased response to Nef for every week postinfection (P = 0.0024), followed by a nonsignificant increase to Pol (4.6%) and Gag (3.2%). Responses to Env and regulatory proteins appeared to remain stable. Three temporal patterns of HIV-specific T-cell responses could be distinguished: persistent, lost, or new. The proportion of persistent T-cell responses was significantly lower (P = 0.0037) in individuals defined as rapid progressors than in those progressing slowly and who controlled viremia. Almost 90% of lost T-cell responses were coincidental with autologous viral epitope escape. Regression analysis between the time to fixed viral escape and lost T-cell responses (r = 0.61; P = 0.019) showed a mean delay of 14 weeks after viral escape. Collectively, T-cell epitope recognition is not a static event, and temporal patterns of IFN-γ-based responses exist. This is due partly to viral sequence variation but also to the recognition of invariant viral epitopes that leads to waves of persistent T-cell immunity, which appears to associate with slower disease progression in the first year of infection.
Figures


References
-
- Allen, T. M., M. Altfeld, S. C. Geer, E. T. Kalife, C. Moore, K. M. O'Sullivan, I. Desouza, M. E. Feeney, R. L. Eldridge, E. L. Maier, D. E. Kaufmann, M. P. Lahaie, L. Reyor, G. Tanzi, M. N. Johnston, C. Brander, R. Draenert, J. K. Rockstroh, H. Jessen, E. S. Rosenberg, S. A. Mallal, and B. D. Walker. 2005. Selective escape from CD8+ T-cell responses represents a major driving force of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) sequence diversity and reveals constraints on HIV-1 evolution. J. Virol. 79:13239-13249. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Altfeld, M., M. M. Addo, R. Shankarappa, P. K. Lee, T. M. Allen, X. G. Yu, A. Rathod, J. Harlow, K. O'Sullivan, M. N. Johnston, P. J. Goulder, J. I. Mullins, E. S. Rosenberg, C. Brander, B. Korber, and B. D. Walker. 2003. Enhanced detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific T-cell responses to highly variable regions by using peptides based on autologous virus sequences. J. Virol. 77:7330-7340. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barouch, D. H., J. Kunstman, M. J. Kuroda, J. E. Schmitz, S. Santra, F. W. Peyerl, G. R. Krivulka, K. Beaudry, M. A. Lifton, D. A. Gorgone, D. C. Montefiori, M. G. Lewis, S. M. Wolinsky, and N. L. Letvin. 2002. Eventual AIDS vaccine failure in a rhesus monkey by viral escape from cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 415:335-339. - PubMed
-
- Berger, C. T., J. M. Carlson, C. J. Brumme, K. L. Hartman, Z. L. Brumme, L. M. Henry, P. C. Rosato, A. Piechocka-Trocha, M. A. Brockman, P. R. Harrigan, D. Heckerman, D. E. Kaufmann, and C. Brander. 2010. Viral adaptation to immune selection pressure by HLA class I-restricted CTL responses targeting epitopes in HIV frameshift sequences. J. Exp. Med. 207:61-75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

