IFN-γ and IL-17: the two faces of T-cell pathology in giant cell arteritis
- PMID: 20827207
- PMCID: PMC3081721
- DOI: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32833ee946
IFN-γ and IL-17: the two faces of T-cell pathology in giant cell arteritis
Abstract
Purpose of review: Granuloma formation in giant cell arteritis (GCA) emphasizes the role of adaptive immunity and highlights the role of antigen-specific T cells. Recent data demonstrate that at least two separate lineages of CD4 T cells participate in vascular inflammation, providing an important clue that multiple disease instigators may initiate pathogenic immunity.
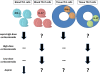
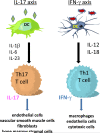
Recent finding: IFN-γ-producing Th1 cells and IL-17-producing Th17 cells have been implicated in GCA. Patients with biopsy-positive GCA underwent two consecutive temporal artery biopsies, one prior to therapy and one while on corticosteroids. In untreated patients, Th1 and Th17 cells co-existed in the vascular lesions. Following therapy, Th17 cells were essentially lost, whereas Th1 cells persisted almost unaffected. In the peripheral blood of untreated patients Th17 frequencies were increased eight-fold, but normalized with therapy. Blood Th1 cells were doubled in frequency, independent of therapy. Corticosteroids functioned by selectively suppressing IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-23-releasing antigen-presenting cells (APCs), disrupting induction of Th17 cells.
Summary: At least two distinct CD4 T-cell subsets promote vascular inflammation in GCA. In early disease, APCs promote differentiation of Th17 as well as Th1 cells. Chronic disease is characterized by persistent Th1-inducing signals, independent of IL-17-mediated inflammation. More than one disease instigator may trigger APCs to induce multiple T-cell lineages. Cocktails of therapies will be needed for appropriate disease control.
Figures
References
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Medium- and large-vessel vasculitis. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:160–169. - PubMed
-
- Saunders BM, Cooper AM. Restraining mycobacteria: role of granulomas in mycobacterial infections. Immunol Cell Biol. 2000;78:334–341. - PubMed
-
- Duhaut P, Bosshard S, Ducroix JP. Is giant cell arteritis an infectious disease? Biological and epidemiological evidence. Presse Med. 2004;33:1403–1408. - PubMed
-
- Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ. Giant cell arteritis as an antigen-driven disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1995;21:1027–1039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

