MicroRNA-21 is involved in ionizing radiation-promoted liver carcinogenesis
- PMID: 20827319
- PMCID: PMC2929947
MicroRNA-21 is involved in ionizing radiation-promoted liver carcinogenesis
Abstract
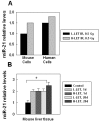
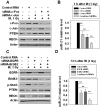
It has been known for decades that ionizing radiation (IR) promotes carcinogenesis and high-linear energy transfer (LET) IR has a higher risk than low-LET IR for carcinogenesis; however, the mechanism remains unclear. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have a critical effect on carcinogenesis through post-transcriptional modification. In this study, our purpose is to explore whether miRNAs are involved in IR-(especially high-LET IR) promoted liver carcinogenesis. We showed here that among several hundred miRNAs, miR-21 was the only one that increased 6 folds in high-LET IR-promoted mouse liver tumors when compared with that in the non-irradiated liver tissues. We also showed that miR-21 was up-regulated in human or mouse hepatocytes after exposure to IR, as well as in liver tissues derived from whole body irradiated mice. The increased level of miR-21 was more significant in high-LET irradiated cells or liver tissues. After the non-irradiated, low-LET or high-LET irradiated human hepatocytes were over-expressed with miR-21, these cells became tumorigenesis in nude mice. The tumors derived from high-LET-irradiated-cells were largest, and accompanied by more significant changes in the miR-21-targets: PTEN and RECK. In addition, we showed that IR-induced up-regulation of miR-21 depended on the up-regulation/activation of AP-1 (at an earlier time, within 2 h) and the ErbB/Stat3 pathway (at a later time, more than 2 h), which was also IR dose dependent. Taken together, we conclude that IR-induced up-regulation of miR-21 plays an important role in IR (especially high-LET IR)-promoted liver carcinogenesis.
Keywords: carcinogenesis; ionizing radiation; miR-21; microRNA.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-21 is continually elevated long-term in the brain after exposure to ionizing radiation.Radiat Res. 2012 Jan;177(1):124-8. doi: 10.1667/rr2764.1. Epub 2011 Oct 28. Radiat Res. 2012. PMID: 22034847
-
Radiation-induced micro-RNA modulation in glioblastoma cells differing in DNA-repair pathways.DNA Cell Biol. 2010 Sep;29(9):553-61. doi: 10.1089/dna.2009.0978. DNA Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20380575
-
Alterations in microRNAs miR-21 and let-7a correlate with aberrant STAT3 signaling and downstream effects during cervical carcinogenesis.Mol Cancer. 2015 Jun 9;14:116. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0385-2. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26051842 Free PMC article.
-
Embryonic stem cell microRNAs: defining factors in induced pluripotent (iPS) and cancer (CSC) stem cells?Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009 Sep;4(3):168-77. doi: 10.2174/157488809789057400. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2009. PMID: 19492978 Review.
-
MicroRNA Changes in Gastric Carcinogenesis: Differential Dysregulation during Helicobacter pylori and EBV Infection.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;12(4):597. doi: 10.3390/genes12040597. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921696 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of microRNA-mediated MMP regulation in the treatment and diagnosis of malignant tumors.Cancer Biol Ther. 2013 Sep;14(9):796-805. doi: 10.4161/cbt.25936. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Cancer Biol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23917402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of Sonic Hedgehog Gene Repressed Irradiation-induced Cellular Senescence in Salivary Glands by Promoting DNA Repair and Reducing Oxidative Stress.Theranostics. 2018 Jan 13;8(4):1159-1167. doi: 10.7150/thno.23373. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29464006 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-Induced Reactions in The Liver - Modulation of Radiation Effects by Lifestyle-Related Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 3;19(12):3855. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123855. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30513990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High Energy Particle Radiation-associated Oncogenic Transformation in Normal Mice: Insight into the Connection between Activation of Oncotargets and Oncogene Addiction.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 23;6:37623. doi: 10.1038/srep37623. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27876887 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-21 modulates the levels of reactive oxygen species by targeting SOD3 and TNFα.Cancer Res. 2012 Sep 15;72(18):4707-13. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0639. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22836756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Redpath J, Antoniono R. Induction of an Adaptive Response against Spontaneous Neoplastic Transformation In Vitro by Low-Dose Gamma Radiation. Radiat Res. 1998;149:517–520. - PubMed
-
- Mitchel R, Jackson J, Carlisle S. Upper Dose Thresholds for Radiation-Induced Adaptive Response against Cancer in High-Dose-Exposed, Cancer-Prone, Radiation-Sensitive Trp53 Heterozygous Mice. Radiat Res. 2004;162:20–30. - PubMed
-
- Little JB. Radiation carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:397–404. - PubMed
-
- Wakeford R. The cancer epidemiology of radiation. Oncogene. 2004;23:6404–6428. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
