Dutasteride prevents the growth response to testosterone in benign and androgen-sensitive malignant prostate cells
- PMID: 20827322
- PMCID: PMC2929950
Dutasteride prevents the growth response to testosterone in benign and androgen-sensitive malignant prostate cells
Abstract
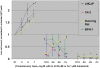
We show that the dual 5-α reductase enzyme inhibitor dutasteride prevents enhanced growth of both benign and malignant prostate cell lines, incubated with physiologic to supraphysiologic doses of testosterone. Using androgen-sensitive benign BPH-1 cells, LNCaP cancer cells, their derivative C4-2 cells, or Dunning rat cancer cells, we subjected 30,000 cells/well to concomitant treatment with 10(-9), 10(-8), or 10(-7) M testosterone in the presence of low (0.25 μM) or high (1.0 μM) doses of dutasteride. Both low- and high-dose dutasteride abrogated testosterone-stimulated growth of all 4 cell lines. If the in vitro data mimic conditions in men undergoing testosterone replacement, concomitant dutasteride use might make testosterone safe for men with benign prostatic hypertrophy, latent prostate cancer and perhaps even aggressive prostate cancer. Testosterone might also be used to prevent the rare anti-androgen side effects of dutasteride when used for benign prostatic hypertrophy and baldness. Further clinical investigation is indicated.
Keywords: BPH; Prostate cancer; dutasteride; testosterone.
Figures
References
-
- Soos G, Tsakiris I, Szanto J, Turzo C, Haas PG, Dezso B. The prevalence of prostate carcinoma and its precursor in Hungary: an autopsy study. Eur Urol. 2005;48:739–44. - PubMed
-
- Stamatiou K, Alevizos A, Agapitos E, Sofras F. Incidence of impalpable carcinoma of the prostate and of non-malignant and precarcinoma-tous lesions in Greek male population: an autopsy study. Prostate. 2006;66:1319–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
