Identification and molecular characterization of a new member of the peritrophic membrane proteins from the meadow moth, loxostege sticticalis
- PMID: 20827401
- PMCID: PMC2935671
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.6.491
Identification and molecular characterization of a new member of the peritrophic membrane proteins from the meadow moth, loxostege sticticalis
Abstract
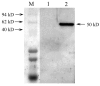
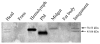
The peritrophic membrane (PM) plays an important role in protecting insects. The PM proteins are important to determinate the formation and function of the PM. A new PM protein, named Lsti99, was identified from the PM of Loxostege sticticalis larvae by cDNA library screening. The full cDNA of Lsti99 is 1392 bp in length, contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 1245 bp that encodes a preprotein of 415 amino acid residues with a 17-amino acid signal peptide. The sequence of Lsti99 showed no homology to other known PM proteins. The recombinant Lsti99 was successfully expressed in insect cells (Sf9) using recombinant baculoviruses and was used to isolate the antibodies to Lsti99 from the polyclonal antiserum. Lsti99 was expressed mainly in the PM, but weaker bands could be detected in the head and integument as well. The Lsti99 protein could be separated from the PM complex by chitinase in vitro, but M2R did not show effect in vitro confirming the chitin-binding activity of Lsti99. The biochemical and physiological functions of Lsti99 in L. sticticalis require further investigation.
Keywords: Chitin-binding activity; Loxostege sticticalis; Lsti99.; Peritrophic membrane protein; Recombinant protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and molecular characterization of a chitin-binding protein from the beet webworm, Loxostege sticticalis L.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Oct 22;15(10):19147-61. doi: 10.3390/ijms151019147. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25340980 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of two new peritrophic membrane proteins from larval Trichoplusia ni: structural characteristics and their functions in the protease rich insect gut.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Mar;34(3):215-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2003.10.001. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14871618
-
Isolation and identification of insect intestinal mucin HaIIM86--the new target for Helicoverpa armigera biocontrol.Int J Biol Sci. 2011 Mar 19;7(3):286-96. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.7.286. Int J Biol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21448339 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Mamestra configurata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) peritrophic matrix proteins and enzymes involved in peritrophic matrix chitin metabolism.Insect Sci. 2016 Oct;23(5):656-74. doi: 10.1111/1744-7917.12225. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Insect Sci. 2016. PMID: 25846407
-
Molecular cloning and functional expression of chitinase-encoding cDNA from the cabbage moth, Mamestra brassicae.Mol Cells. 2012 May;33(5):439-47. doi: 10.1007/s10059-012-2133-4. Epub 2011 Nov 25. Mol Cells. 2012. PMID: 22124732 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of a peritrophic membrane protein from the silkworm, Bombyx mori.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Feb;40(2):1087-95. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2151-5. Epub 2012 Oct 14. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23065286
-
A new type I peritrophic membrane protein from larval Holotrichia oblita (Coleoptera: Melolonthidae) binds to chitin.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Apr 22;15(4):6831-42. doi: 10.3390/ijms15046831. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24758927 Free PMC article.
-
Novel insights into the insect trancriptome response to a natural DNA virus.BMC Genomics. 2015 Apr 17;16(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1499-z. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25924671 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of general odorant binding protein 2 from the meadow moth, Loxostege sticticalis L. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae).PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033589. Epub 2012 Mar 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22479417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lehane MJ. Peritrophic matrix structure and function. Annu Rev Entomol. 1997;42:525–50. - PubMed
-
- Tellam RL, Wijffels G, Willadsen P. Peritrophic membrane proteins. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 1999;29:87–101. - PubMed
-
- Bolognesi R, Ribeiro AF, Terra WR. et al.The peritrophic membrane of Spodoptera frugiperda: secretion of peritrophins and role in immobilization and recycling digestive enzymes. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2001;47:62–75. - PubMed
-
- Pascoa V, Oliveira PL, Dansa-Petretski M. et al.Aedes aegypti peritrophic matrix and its interaction with heme during blood digestion. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;32:517–23. - PubMed
-
- Kato N, Dasgupta R, Smartt C. et al.Glucosamine: fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase: gene characterization, chitin biosynthesis and peritrophic matrix formation in Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol Biol. 2002;11:207–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

