Long range dynamic effects of point-mutations trap a response regulator in an active conformation
- PMID: 20828564
- PMCID: PMC2949504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.08.051
Long range dynamic effects of point-mutations trap a response regulator in an active conformation
Abstract
When a point-mutation in a protein elicits a functional change, it is most common to assign this change to local structural perturbations. Here we show that point-mutations, distant from an essential highly dynamic kinase recognition loop in the response regulator Spo0F, lock this loop in an active conformation. This 'conformational trapping' results in functionally hyperactive Spo0F. Consequently, point-mutations are seen to affect functionally critical motions both close to and far from the mutational site.
Copyright © 2010 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

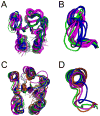

 ” Spo0F; red “
” Spo0F; red “ ” Spo0F-BeF3; orange “
” Spo0F-BeF3; orange “ ” L66A; purple “
” L66A; purple “ ” I90A; black “*” H101A.
” I90A; black “*” H101A.Similar articles
-
Predominantly buried residues in the response regulator Spo0F influence specific sensor kinase recognition.FEBS Lett. 2007 Apr 3;581(7):1425-9. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.02.061. Epub 2007 Mar 5. FEBS Lett. 2007. PMID: 17350627 Free PMC article.
-
Alanine mutants of the Spo0F response regulator modifying specificity for sensor kinases in sporulation initiation.Mol Microbiol. 1999 Jul;33(2):389-95. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1999.01481.x. Mol Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10411754
-
Molecular recognition in signal transduction: the interaction surfaces of the Spo0F response regulator with its cognate phosphorelay proteins revealed by alanine scanning mutagenesis.J Mol Biol. 1997 Sep 19;272(2):200-12. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1226. J Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9299348
-
Molecular recognition of bacterial phosphorelay proteins.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;5(2):142-8. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(02)00305-3. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11934609 Review.
-
Identification of communication networks in Spo0F: a model for phosphorylation-induced conformational change and implications for activation of multiple domain bacterial response regulators.FEBS Lett. 1998 Mar 20;425(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00182-3. FEBS Lett. 1998. PMID: 9540996 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Position K+4 in the Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation Reaction Kinetics of the CheY Response Regulator.Biochemistry. 2021 Jul 6;60(26):2130-2151. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00246. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 34167303 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the Francisella response regulator QseB receiver domain, and characterization of QseB inhibition by antibiofilm 2-aminoimidazole-based compounds.Mol Microbiol. 2017 Oct;106(2):223-235. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13759. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Mol Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28755524 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics and activation in response regulators: the β4-α4 loop.Biomol Concepts. 2012 Feb 1;3(2):175-182. doi: 10.1515/bmc-2011-0063. Biomol Concepts. 2012. PMID: 24494032 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of atomic displacement parameters in bovine trypsin reveals a distributed lattice of atoms with shared chemical properties.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 17;9(1):19281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55777-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31848402 Free PMC article.
-
Toward rationally redesigning bacterial two-component signaling systems using coevolutionary information.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 4;111(5):E563-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323734111. Epub 2014 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24449878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoch JA, Silhavy TJ. Two-component signal transduction. ASM Press; Washington, D.C: 1995.
-
- Hoch JA. Two-component and phosphorelay signal transduction. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000;3:165–70. - PubMed
-
- Sharp JS, Sullivan DM, Cavanagh J, Tomer KB. Measurement of multisite oxidation kinetics reveals an active site conformational change in Spo0F as a result of protein oxidation. Biochemistry. 2006;45:6260–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

