Apolipoprotein CIII induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin 6 expression via Toll-like receptor 2 pathway in mouse adipocytes
- PMID: 20829510
- PMCID: PMC3203842
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.210427
Apolipoprotein CIII induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin 6 expression via Toll-like receptor 2 pathway in mouse adipocytes
Retraction in
-
Notice of retraction. Apolipoprotein CIII induces monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and interleukin 6 expression via Toll-like receptor 2 pathway in mouse adipocytes.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012 Mar;32(3):e22. doi: 10.1161/ATV.0b013e31824cc102. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012. PMID: 22345596 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To examine the direct effect of apolipoprotein CIII (apoCIII) on adipokine expressions that are involved in obesity, insulin resistance, or metabolic syndrome.
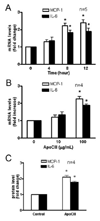
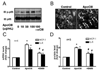
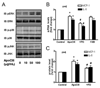
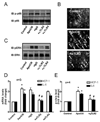
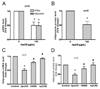
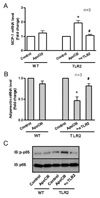
Methods and results: ApoCIII in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins is elevated in patients with obesity, insulin resistance, or metabolic syndrome. Its level is also associated with proinflammatory adipokines. Fully differentiated mouse 3T3L1 adipocytes were incubated with apoCIII. ApoCIII activated nuclear factor κB of 3T3L1 adipocytes and induced the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP) 1 and interleukin (IL) 6. ApoCIII also activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK)-1 inhibitor PD98059, but not p38 inhibitor SB203580, inhibited apoCIII-induced upregulation of MCP-1 and IL-6. Previously, it was shown that apoCIII activates proinflammatory signals through toll-like receptor (TLR) 2. TLR2-blocking antibody abolished activation of nuclear factor κB and extracellular signal-regulated kinase induced by apoCIII and inhibited apoCIII-induced upregulation of MCP-1 and IL-6. ApoCIII also reduced adiponectin expression of 3T3L1 adipocytes, which was recovered by TLR2-blocking antibody. ApoCIII induced the expression of MCP-1 and IL-6 in TLR2-overexpressed human embryonic kidney 293 cells but not wild-type human embryonic kidney 293 cells without TLR2. ApoCIII induced the expression of MCP-1 and IL-6 and decreased adiponectin expression in white adipose tissue of wild-type mice but not of TLR2-deficient mice in vivo.
Conclusions: ApoCIII may activate extracellular signal-regulated kinase and nuclear factor kB through TLR2 and induce proinflammatory adipokine expression in vitro and in vivo. Thus, apoCIII links dyslipidemia to inflammation in adipocytes, which, in turn, may contribute to atherosclerosis.
Figures
References
-
- Ginsberg HN, Le NA, Goldberg IJ, Gibson JC, Rubinstein A, Wang-Iverson P, Norum R, Brown WV. Apolipoprotein B metabolism in subjects with deficiency of apolipoproteins CIII and AI: evidence that apolipoprotein CIII inhibits catabolism of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by lipoprotein lipase in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1986;78:1287–1295. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aalto-Setala K, Fisher EA, Chen X, Chajek-Shaul T, Hayek T, Zechner R, Walsh A, Ramakrishnan R, Ginsberg HN, Breslow JL. Mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia in human apolipoprotein (apo) CIII transgenic mice: diminished very low density lipoprotein fractional catabolic rate associated with increased apo CIII and reduced apo E on the particles. J Clin Invest. 1992;90:1889–1900. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan DC, Watts GF, Nguyen MN, Barrett PH. Apolipoproteins C-III and A-V as predictors of very-low-density lipoprotein triglyceride and apolipoprotein B-100 kinetics. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:590–596. - PubMed
-
- Zheng C, Khoo C, Ikewaki K, Sacks FM. Rapid turnover of apolipoprotein C-III-containing triglyceride-rich lipoproteins contributing to the formation of LDL subfractions. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:1190–1203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

