Graphic reanalysis of the two NINDS-tPA trials confirms substantial treatment benefit
- PMID: 20829518
- PMCID: PMC2949055
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.583807
Graphic reanalysis of the two NINDS-tPA trials confirms substantial treatment benefit
Abstract
Background and purpose: Multiple statistical analyses of the 2 NINDS-tPA trials have confirmed study findings of benefit of fibrinolytic therapy. A recent graphic analysis departed from best practices in the visual display of quantitative information by failing to take into account the skewed functional importance of NIH Stroke Scale raw scores and by scaling change axes at up to 20 times the range achievable by individual patients.
Methods: Using the publicly available datasets of the 2 NINDS-tPA trials, we generated a variety of figures appropriate to the characteristics of acute stroke trial data.
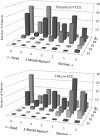
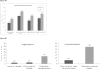
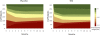
Results: A diverse array of figures all visually delineated substantial benefits of fibrinolytic therapy, including: bar charts of normalized gain and loss; stacked bar, bar, and matrix plots of clinically relevant ordinal ranks; a time series stacked line plot of continuous scale disability weights; and line plot, bubble chart, and person icon array graphs of joint outcome table analysis. The achievable change figure showed substantially greater improvement among tPA than placebo patients, median 66.7% (interquartile range, 0 to 92.0) versus 50.0% (interquartile range, -7.1 to 80.0), P=0.003.
Conclusions: On average, under 3 hour patients treated with tPA recovered two-thirds while placebo patients improved only half of the way toward fully normal. Graphical analyses of the 2 NINDS-tPA trials, when performed according to best practices, is a useful means of conveying details about patient response to therapy not fully delineated by summary statistics, and confirms a valuable treatment benefit of under 3 hour fibrinolytic therapy in acute stroke.
Figures



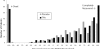

References
-
- Tufte E. The Visual Display of Quantitative Information. 2nd ed. Graphics Press LLC; Cheshire, Connecticut: 2001.
-
- Hoffman JR, Schriger DL. A graphic reanalysis of the NINDS Trial [sic] Ann Emerg Med. 2009;54:329–336. 336, e321–335. - PubMed
-
- NINDS rt-PA Stroke Group Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. New England Journal of Medicine. 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Ingall TJ, O'Fallon WM, Asplund K, Goldfrank LR, Hertzberg VS, Louis TA, Christianson TJ. Findings from the reanalysis of the NINDS tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke treatment trial. Stroke. 2004;35:2418–2424. - PubMed
-
- Adams HP, Jr., del Zoppo G, Alberts MJ, Bhatt DL, Brass L, Furlan A, Grubb RL, Higashida RT, Jauch EC, Kidwell C, Lyden PD, Morgenstern LB, Qureshi AI, Rosenwasser RH, Scott PA, Wijdicks EF. Guidelines for the early management of adults with ischemic stroke: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, Clinical Cardiology Council, Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention Council, and the Atherosclerotic Peripheral Vascular Disease and Quality of Care Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Groups: the American Academy of Neurology affirms the value of this guideline as an educational tool for neurologists. Stroke. 2007;38:1655–1711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

