Long-term IGF-I exposure decreases autophagy and cell viability
- PMID: 20830296
- PMCID: PMC2935370
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012592
Long-term IGF-I exposure decreases autophagy and cell viability
Abstract
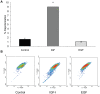
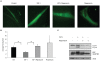
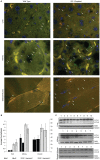
A reduction in IGF-I signaling has been found to increase lifespan in multiple organisms despite the fact that IGF-I is a trophic factor for many cell types and has been found to have protective effects against multiple forms of damage in acute settings. The increase in longevity seen in response to reduced IGF-I signaling suggests that there may be differences between the acute and chronic impact of IGF-I signaling. We have examined the possibility that long-term stimulation with IGF-I may have a negative impact at the cellular level using quiescent human fibroblasts. We find that fibroblast cells exposed to IGF-I for 14 days have reduced long-term viability as judged by colony forming assays, which is accompanied by an accumulation of senescent cells. In addition we observe an accumulation of cells with depolarized mitochondria and a reduction in autophagy in the long-term IGF-I treated cultures. An examination of mice with reduced IGF-I levels reveals evidence of enhanced autophagy and fibroblast cells derived from these mice have a larger mitochondrial mass relative to controls indicating that changes in mitochondrial turnover occurs in animals with reduced IGF-I. The results indicate that chronic IGF-I stimulation leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced cell viability.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



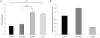

References
-
- Smith PJ, Wise LS, Berkowitz R, Wan C, Rubin CS. Insulin-like growth factor-I is an essential regulator of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988;263:9402–9408. - PubMed
-
- Tollefsen SE, Lajara R, McCusker RH, Clemmons DR, Rotwein P. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in muscle development. Expression of IGF-I, the IGF-I receptor, and an IGF binding protein during myoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:13810–13817. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Florini JR, Ewton DZ, Coolican SA. Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis. Endocr Rev. 1996;17:481–517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

