Kinin B1 receptor enhances the oxidative stress in a rat model of insulin resistance: outcome in hypertension, allodynia and metabolic complications
- PMID: 20830306
- PMCID: PMC2935380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012622
Kinin B1 receptor enhances the oxidative stress in a rat model of insulin resistance: outcome in hypertension, allodynia and metabolic complications
Abstract
Background: Kinin B(1) receptor (B(1)R) is induced by the oxidative stress in models of diabetes mellitus. This study aims at determining whether B(1)R activation could perpetuate the oxidative stress which leads to diabetic complications.
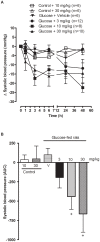
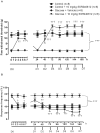
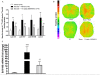
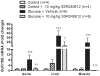
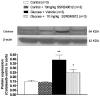
Methods and findings: Young Sprague-Dawley rats were fed with 10% D-Glucose or tap water (controls) for 8-12 weeks. A selective B(1)R antagonist (SSR240612) was administered acutely (3-30 mg/kg) or daily for a period of 7 days (10 mg/kg) and the impact was measured on systolic blood pressure, allodynia, protein and/or mRNA B(1)R expression, aortic superoxide anion (O(2)(*-)) production and expression of superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) and catalase. SSR240612 reduced dose-dependently (3-30 mg/kg) high blood pressure in 12-week glucose-fed rats, but had no effect in controls. Eight-week glucose-fed rats exhibited insulin resistance (HOMA index), hypertension, tactile and cold allodynia and significant increases of plasma levels of glucose and insulin. This was associated with higher aortic levels of O(2)(*-), NADPH oxidase activity, MnSOD and catalase expression. All these abnormalities including B(1)R overexpression (spinal cord, aorta, liver and gastrocnemius muscle) were normalized by the prolonged treatment with SSR240612. The production of O(2)(*-) in the aorta of glucose-fed rats was also measured in the presence and absence of inhibitors (10-100 microM) of NADPH oxidase (apocynin), xanthine oxidase (allopurinol) or nitric oxide synthase (L-NAME) with and without Sar[D-Phe(8)]des-Arg(9)-BK (20 microM; B(1)R agonist). Data show that the greater aortic O(2)(*-) production induced by the B(1)R agonist was blocked only by apocynin.
Conclusions: Activation of kinin B(1)R increased O(2)(*-) through the activation of NADPH oxidase in the vasculature. Prolonged blockade of B(1)R restored cardiovascular, sensory and metabolic abnormalities by reducing oxidative stress and B(1)R gene expression in this model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Blockade of sensory abnormalities and kinin B(1) receptor expression by N-acetyl-L-cysteine and ramipril in a rat model of insulin resistance.Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Jul 28;589(1-3):66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 May 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18555989
-
The kinin B1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 reverses tactile and cold allodynia in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;152(2):280-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707388. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17618300 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of kinin B1 receptor and oxidative stress in sensory abnormalities and arterial hypertension in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance.Neuropeptides. 2007 Dec;41(6):375-87. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2007.09.005. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Neuropeptides. 2007. PMID: 17988733
-
Putative roles of kinin receptors in the therapeutic effects of angiotensin 1-converting enzyme inhibitors in diabetes mellitus.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Oct 1;500(1-3):467-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.07.045. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15464053 Review.
-
The kinin system mediates hyperalgesia through the inducible bradykinin B1 receptor subtype: evidence in various experimental animal models of type 1 and type 2 diabetic neuropathy.Biol Chem. 2006 Feb;387(2):127-43. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.018. Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16497144 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiac inflammation after local irradiation is influenced by the kallikrein-kinin system.Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 1;72(19):4984-92. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1831. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22865451 Free PMC article.
-
Bradykinin Type 1 Receptor - Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase: A New Axis Implicated in Diabetic Retinopathy.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Mar 29;10:300. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00300. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30983997 Free PMC article.
-
Kininase 1 As a Preclinical Therapeutic Target for Kinin B1 Receptor in Insulin Resistance.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 2;8:509. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00509. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28824433 Free PMC article.
-
Neuro-Immunity Controls Obesity-Induced Pain.Front Hum Neurosci. 2020 Jun 9;14:181. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2020.00181. eCollection 2020. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32581740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of pioglitazone and bradykinin type 1 receptor antagonist on type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice.Obes Sci Pract. 2017 Jul 6;3(3):352-362. doi: 10.1002/osp4.117. eCollection 2017 Sep. Obes Sci Pract. 2017. PMID: 29071111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lungu C, Dias JP, Franca CE, Ongali B, Regoli D, et al. Involvement of kinin B1 receptor and oxidative stress in sensory abnormalities and arterial hypertension in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance. Neuropeptides. 2007;41:375–387. - PubMed
-
- Ismael MA, Talbot S, Carbonneau CL, Beausejour CM, Couture R. Blockade of sensory abnormalities and kinin B(1) receptor expression by N-acetyl-L-cysteine and ramipril in a rat model of insulin resistance. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;589:66–72. - PubMed
-
- Marceau F, Sabourin T, Houle S, Fortin JP, Petitclerc E, et al. Kinin receptors: functional aspects. Int Immunol. 2002;2:1729–1739. - PubMed
-
- Couture R, Girolami JP. Putative roles of kinin receptors in the therapeutic effects of angiotensin 1-converting enzyme inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;500:467–485. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

