Extensions to the Speech Disorders Classification System (SDCS)
- PMID: 20831378
- PMCID: PMC2941221
- DOI: 10.3109/02699206.2010.503006
Extensions to the Speech Disorders Classification System (SDCS)
Abstract
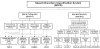
This report describes three extensions to a classification system for paediatric speech sound disorders termed the Speech Disorders Classification System (SDCS). Part I describes a classification extension to the SDCS to differentiate motor speech disorders from speech delay and to differentiate among three sub-types of motor speech disorders. Part II describes the Madison Speech Assessment Protocol (MSAP), an ∼ 2-hour battery of 25 measures that includes 15 speech tests and tasks. Part III describes the Competence, Precision, and Stability Analytics (CPSA) framework, a current set of ∼ 90 perceptual- and acoustic-based indices of speech, prosody, and voice used to quantify and classify sub-types of Speech Sound Disorders (SSD). A companion paper provides reliability estimates for the perceptual and acoustic data reduction methods used in the SDCS. The agreement estimates in the companion paper support the reliability of SDCS methods and illustrate the complementary roles of perceptual and acoustic methods in diagnostic analyses of SSD of unknown origin. Examples of research using the extensions to the SDCS described in the present report include diagnostic findings for a sample of youth with motor speech disorders associated with galactosemia, and a test of the hypothesis of apraxia of speech in a group of children with autism spectrum disorders. All SDCS methods and reference databases running in the PEPPER (Programs to Examine Phonetic and Phonologic Evaluation Records) environment will be disseminated without cost when complete.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bishop DVM. Motor immaturity and specific speech and language impairment: Evidence for a common genetic basis. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 2002;114:56–63. - PubMed
-
- Bradford A, Murdoch B, Thompson E, Stokes P. Lip and tongue function in children with developmental speech disorders: A preliminary investigation. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics. 1997;11:363–387.
-
- Broomfield J, Dodd B. The nature of referred subtypes of primary speech disability. Child Language Teaching and Therapy. 2004;20:135–151.
-
- Campbell TF, Dollaghan CA, Rockette HE, Paradise JL, Feldman HM, Shriberg LD, et al. Risk factors for speech delay of unknown origin in 3-year-old children. Child Development. 2003;74:346–357. - PubMed
-
- Cheng HC, Chen HY, Tsai CL, Chen YJ, Cherng RJ. Comorbidity of motor and language impairments in preschool children of Taiwan. Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2009;30:1054–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
