Stage IV marginal zone B-cell lymphoma--prognostic factors and the role of rituximab: Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL) study
- PMID: 20831770
- PMCID: PMC11159655
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01698.x
Stage IV marginal zone B-cell lymphoma--prognostic factors and the role of rituximab: Consortium for Improving Survival of Lymphoma (CISL) study
Abstract
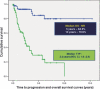
Stage IV marginal zone B-cell lymphomas (MZL) are detected in more than 25% of lymphoma patients. In this study, we conducted retrospective analyses of specific cases of stage IV MZL in order to assess their clinical features, as well as the treatments and prognoses of these cases. A total of 94 patients with histological diagnosis of stage IV-MZL from 17 different institutions in Korea were included. Multiple-mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)-organs-involved MZL (M-MZL) was detected in 34 patients (36.2%). Bone-marrow-involved stage IV MZL (BM-MZL) was detected in 33 patients (35.1%). Median time to progression (TTP) was 2.4years (95% CI, 1.9-2.9). Five- and 10-year overall survival rates were 84.5% and 79.8%, respectively. Patients with lymph node involvement in stage IV MZL appeared to have worse prognoses in TTP (P=0.015). Thirty-one patients were treated with a regimen including rituximab (CTx-R[+]), and 31 with a regimen that did not include rituximab (CTx-R[-]). The CTx-R(+) group showed better responses than the CTx-R(-) group (83.9%versus 54.8%, P=0.026). However, no differences in TTP duration were detected (P=0.113). Stage IV MZL tend to follow an indolent disease course. Therefore, lymph node involvement is a more valuable prognostic factor for TTP. Rituximab appears to contribute to better responses, but not in cases of TTP.
© 2010 Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Zucca E, Conconi A, Pedrinis E et al. Nongastric marginal zone B‐cell lymphoma of mucosa‐associated lymphoid tissue. Blood 2003; 101: 2489–95. - PubMed
-
- Oh SY, Ryoo BY, Kim WS et al. Nongastric marginal zone B‐cell lymphoma: analysis of 247 cases. Am J Hematol 2007; 82: 446–52. - PubMed
-
- Isaacson PG. Update on MALT lymphomas. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2005; 18: 57–68. - PubMed
-
- Ko YH, Kim CW, Park CS et al. REAL classification of malignant lymphomas in the Republic of Korea: incidence of recently recognized entities and changes in clinicopathologic features. Hematolymphoreticular Study Group of the Korean Society of Pathologists. Revised European‐American lymphoma. Cancer 1998; 83: 806–12. - PubMed
-
- Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M. Report of the Committee on Hodgkin’s Disease Staging Classification. Cancer Res 1971; 31: 1860–1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

