Performance characteristics of the Cavidi ExaVir viral load assay and the ultra-sensitive P24 assay relative to the Roche Monitor HIV-1 RNA assay
- PMID: 20832356
- PMCID: PMC3025774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2010.07.022
Performance characteristics of the Cavidi ExaVir viral load assay and the ultra-sensitive P24 assay relative to the Roche Monitor HIV-1 RNA assay
Abstract
Background: The Cavidi viral load assay and the ultra-sensitive p24 antigen assay (Up24 Ag) have been suggested as more feasible alternatives to PCR-based HIV viral load assays for use in monitoring patients infected with HIV-1 in resource-limited settings.
Objectives: To describe the performance of the Cavidi ExaVir Load™ assay (version 2.0) and two versions of the Up24 antigen assay and to characterize their agreement with the Roche Monitor HIV-1 RNA assay (version 1.5).
Study design: Observational study using a convenience sample of 342 plasma specimens from 108 patients enrolled in two ACTG clinical trials to evaluate the performance characteristics of the Up24 Ag assay using two different lysis buffers and the Cavidi ExaVir Load™ assay.
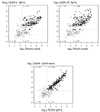
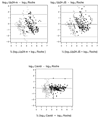
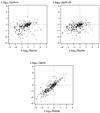
Results: In analysis of agreement with the Roche assay, the Cavidi assay demonstrated superiority to the Up24 Ag assays in accuracy and precision, as well as sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values for HIV-1 RNA ≥ 400, ≥ 1000 and ≥ 5000 copies/mL. Logistic performance curves indicated that the Cavidi assay was superior to the Up24 assays for viral loads greater than 650 copies/mL.
Conclusions: The results suggest that the Cavidi ExaVir Load assay could be used for monitoring HIV-1 viral load in resource-limited settings.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of two human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) RNA surrogate assays to the standard HIV RNA assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Dec;43(12):5950-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.12.5950-5956.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16333081 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of two commercially available, inexpensive alternative assays used for assessing viral load in a cohort of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C-infected patients from South Africa.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43(2):857-61. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.2.857-861.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15695692 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of the ExaVir Load version 3 reverse transcriptase assay for measurement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 plasma load.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Oct;47(10):3266-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00715-09. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19656978 Free PMC article.
-
The measurement of HIV-1 viral load in resource-limited settings: how and where?Clin Lab. 2007;53(3-4):135-48. Clin Lab. 2007. PMID: 17447649 Review.
-
HIV-1 viral load assays for resource-limited settings.PLoS Med. 2006 Oct;3(10):e417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030417. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 17032062 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay for detection and quantification of genetically diverse HIV-1, SIVcpz, and SIVgor strains.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Mar;51(3):787-98. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02792-12. Epub 2012 Dec 19. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23254130 Free PMC article.
-
Can HIV reverse transcriptase activity assay be a low-cost alternative for viral load monitoring in resource-limited settings?BMJ Open. 2016 Jan 27;6(1):e008795. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-008795. BMJ Open. 2016. PMID: 26817634 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Low-cost assays for monitoring HIV infected individuals in resource-limited settings.Indian J Med Res. 2011 Dec;134(6):823-34. doi: 10.4103/0971-5916.92628. Indian J Med Res. 2011. PMID: 22310816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A lateral flow assay for quantitative detection of amplified HIV-1 RNA.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045611. Epub 2012 Sep 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029134 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Cavidi ExaVir Load Assay for Monitoring Plasma Viral Load in HIV-2-Infected Patients.J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Aug;55(8):2367-2379. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00235-17. Epub 2017 May 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28515216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun J, Plantier JC, Hellot MF, Tuaillon E, Gueudin M, Damond F, et al. A new quantitative HIV load assay based on plasma virion reverse transcriptase activity for the different types, groups and subtypes. AIDS. 2003;17:331–336. - PubMed
-
- Ekstrand DH, Awad RJ, Kallander CF, Gronowitz JS. A sensitive assay for the quantification of reverse transcriptase activity based on the use of carrier bound template and non radioactive product detection, with special reference to human immunodeficiency virus isolation. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1996;23(Pt 2):95–105. - PubMed
-
- Greengrass VL, Turnbull SP, Hocking J, Dunne AL, Tachedjian G, Corrigan GE, et al. Evaluation of a low cost reverse transcriptase assay for plasma HIV 1 viral load monitoring. Curr HIV Res. 2005;3:183–190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI50410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1U54RR024383/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025747/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069467/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069467/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI045008/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI069467/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

