Nrg1/ErbB signaling networks in Schwann cell development and myelination
- PMID: 20832498
- PMCID: PMC2991617
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.08.008
Nrg1/ErbB signaling networks in Schwann cell development and myelination
Abstract
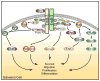
Neuregulin-1 (Nrg1) provides a key axonal signal that regulates Schwann cell proliferation, migration and myelination through binding to ErbB2/3 receptors. The analysis of a number of genetic models has unmasked fundamental mechanisms underlying the specificity of the Nrg1/ErbB signaling axis. Differential expression of Nrg1 isoforms, Nrg1 processing, and ErbB receptor localization and trafficking represent important regulatory themes in the control of Nrg1/ErbB function. Nrg1 binding to ErbB2/3 receptors results in the activation of intracellular signal transduction pathways that initiate changes in Schwann cell behavior. Here, we review data that has defined the role of key Nrg1/ErbB signaling components like Shp2, ERK1/2, FAK, Rac1/Cdc42 and calcineurin in development of the Schwann cell lineage in vivo. Many of these regulators receive converging signals from other cues that are provided by Notch, integrin or G-protein coupled receptors. Signaling by multiple extracellular factors may act as key modifiers and allow Schwann cells at different developmental stages to respond in distinct manners to the Nrg1/ErbB signal.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bargmann CI, Hung MC, Weinberg RA. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986;319(6050):226–30. - PubMed
-
- Downward J, Yarden Y, Mayes E, Scrace G, Totty N, Stockwell P, et al. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984;307(5951):521–7. - PubMed
-
- Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX. Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001;2(2):127–37. - PubMed
-
- Burgess AW, Cho HS, Eigenbrot C, Ferguson KM, Garrett TP, Leahy DJ, et al. An open-and-shut case? Recent insights into the activation of EGF/ErbB receptors. Mol Cell. 2003;12(3):541–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

