Activation of the unfolded protein response by a cataract-associated αA-crystallin mutation
- PMID: 20833134
- PMCID: PMC2956780
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.09.023
Activation of the unfolded protein response by a cataract-associated αA-crystallin mutation
Abstract
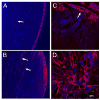
αA-crystallin is a lens chaperone that plays an essential role in the transparency and refractive properties of the lens. Mutations in αA-crystallin have been associated with the development of hereditary cataracts. The R49C mutation of αA-crystallin (αA-R49C) was identified in a four-generation Caucasian family with hereditary cataracts. The αA-R49C protein forms larger-than-normal oligomers in the lens and has decreased solubility. This aberrant αA-R49C oligomerization suggests that protein folding is altered. However, whether activation of the unfolded protein response (UPR) occurs during crystallin mutation-induced cataract formation and whether the UPR causes cell death under these conditions is unclear. We investigated UPR activation in an in vivo mouse model of αA-R49C using immunoblot analysis of lens extracts. We found that expression of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) chaperone, BiP, was 5-fold higher in homozygous αA-R49C lenses than in wild type lenses. Analysis of proteins typically expressed during the UPR revealed that ATF-4 and CHOP levels were also higher in homozygous lenses than in wild type lenses, while the opposite was true of ATF-6 and XBP-1. Taken together, these findings show that mutation of αA-crystallin induces activation of the UPR during cataract formation. They also suggest that the UPR is an important mediator of cell death observed in homozygous αA-R49C lenses.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

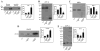
Similar articles
-
Autophagy and UPR in alpha-crystallin mutant knock-in mouse models of hereditary cataracts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt B):234-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26071686 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of insolubilization by a single-point mutation in alphaA-crystallin linked with hereditary human cataracts.Biochemistry. 2008 Sep 9;47(36):9697-706. doi: 10.1021/bi800594t. Epub 2008 Aug 14. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18700785 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of small heat shock protein function in vivo: a knock-in mouse model demonstrates that the R49C mutation in alpha A-crystallin enhances protein insolubility and cell death.J Biol Chem. 2008 Feb 29;283(9):5801-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708704200. Epub 2007 Dec 5. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18056999
-
AlphaA-crystallin R49Cneo mutation influences the architecture of lens fiber cell membranes and causes posterior and nuclear cataracts in mice.BMC Ophthalmol. 2009 Jul 20;9:4. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-9-4. BMC Ophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19619312 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of alpha-crystallin on lens cell function and cataract pathology.Curr Mol Med. 2009 Sep;9(7):887-92. doi: 10.2174/156652409789105598. Curr Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19860667 Review.
Cited by
-
Autophagy and UPR in alpha-crystallin mutant knock-in mouse models of hereditary cataracts.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt B):234-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26071686 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effects of SkQ1 eye drops on cataractogenesis in senescence-accelerated OXYS rats.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015 Feb;253(2):237-48. doi: 10.1007/s00417-014-2806-0. Epub 2014 Sep 30. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 25267419
-
GJA8 missense mutation disrupts hemichannels and induces cell apoptosis in human lens epithelial cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 16;9(1):19157. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55549-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31844091 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomerization with wt αA- and αB-crystallins reduces proteasome-mediated degradation of C-terminally truncated αA-crystallin.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012 May 4;53(6):2541-50. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-9147. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012. PMID: 22427585 Free PMC article.
-
Insights on Human Small Heat Shock Proteins and Their Alterations in Diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 25;9:842149. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.842149. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35281256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaufman RJ. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1211–1233. - PubMed
-
- Bernales S, Papa FR, Walter P. Intracellular signaling by the unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:487–508. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, Yuan J. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature. 2000;403:98–103. - PubMed
-
- Imai Y, Soda M, Inoue H, Hattori N, Mizuno Y, Takahashi R. An unfolded putative transmembrane polypeptide, which can lead to endoplasmic reticulum stress, is a substrate of Parkin. Cell. 2001;105:891–902. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

