Interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 regulation of neural progenitor cell proliferation with hippocampal injury: differential regulatory pathways in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the adolescent and mature mouse brain
- PMID: 20833246
- PMCID: PMC3033445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.09.003
Interleukin (IL)-1 and IL-6 regulation of neural progenitor cell proliferation with hippocampal injury: differential regulatory pathways in the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the adolescent and mature mouse brain
Abstract
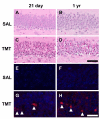
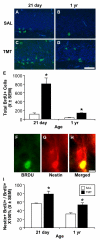
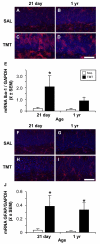
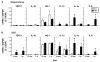
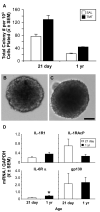
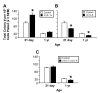
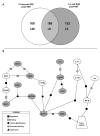
Current data suggests an association between elevations in interleukin 1 (IL-1)α, IL-1β, and IL-6 and the proliferation of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) following brain injury. A limited amount of work implicates changes in these pro-inflammatory responses with diminished NPC proliferation observed as a function of aging. In the current study, adolescent (21day-old) and 1year-old CD-1 male mice were injected with trimethyltin (TMT, 2.3mg/kg, i.p.) to produce acute apoptosis of hippocampal dentate granule cells. In this model, fewer 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine (BrdU)+ NPC were observed in both naive and injured adult hippocampus as compared to the corresponding number seen in adolescent mice. At 48h post-TMT, a similar level of neuronal death was observed across ages, yet activated ameboid microglia were observed in the adolescent and hypertrophic process-bearing microglia in the adult. IL-1α mRNA levels were elevated in the adolescent hippocampus; IL-6 mRNA levels were elevated in the adult. In subgranular zone (SGZ) isolated by laser-capture microdissection, IL-1β was detected but not elevated by TMT, IL-1a was elevated at both ages, while IL-6 was elevated only in the adult. Naïve NPCs isolated from the hippocampus expressed transcripts for IL-1R1, IL-6Rα, and gp130 with significantly higher levels of IL-6Rα mRNA in the adult. In vitro, IL-1α (150pg/ml) stimulated proliferation of adolescent NPCs; IL-6 (10ng/ml) inhibited proliferation of adolescent and adult NPCs. Microarray analysis of SGZ post-TMT indicated a prominence of IL-1a/IL-1R1 signaling in the adolescent and IL-6/gp130 signaling in the adult.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ajmone-Cat MA, Cacci E, Ragazzoni Y, Minghetti L, Biagioni S. Pro-gliogenic effect of IL-1alpha in the differentiation of embryonic neural precursor cells in vitro. J Neurochem. 2010;113:1060–1072. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Buylla A, Lim DA. For the long run: maintaining germinal niches in the adult brain. Neuron. 2004;41:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Banasr M, Hery M, Printemps R, Daszuta A. Serotonin-induced increases in adult cell proliferation and neurogenesis are mediated through different and common 5-HT receptor subtypes in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2004;29:450–460. - PubMed
-
- Ben Abdallah NM, Slomianka L, Vyssotski AL, Lipp HP. Early age-related changes in adult hippocampal neurogenesis in C57 mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:151–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

