Reactive oxygen species and the brain in sleep apnea
- PMID: 20833273
- PMCID: PMC3088760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2010.09.001
Reactive oxygen species and the brain in sleep apnea
Abstract
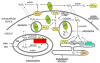
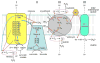
Rodents exposed to intermittent hypoxia (IH), a model of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), manifest impaired learning and memory and somnolence. Increased levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), oxidative tissue damage, and apoptotic neuronal cell death are associated with the presence of IH-induced CNS dysfunction. Furthermore, treatment with antioxidants or overexpression of antioxidant enzymes is neuroprotective during IH. These findings mimic clinical cases of OSA and suggest that ROS may play a key causal role in OSA-induced neuropathology. Controlled production of ROS occurs in multiple subcellular compartments of normal cells and de-regulation of such processes may result in excessive ROS production. The mitochondrial electron transport chain, especially complexes I and III, and the NADPH oxidase in the cellular membrane are the two main sources of ROS in brain cells, although other systems, including xanthine oxidase, phospholipase A2, lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450, may all play a role. The initial evidence for NADPH oxidase and mitochondrial involvement in IH-induced ROS production and neuronal injury unquestionably warrants future research efforts.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
NLRP3 Deficiency Protects Against Intermittent Hypoxia-Induced Neuroinflammation and Mitochondrial ROS by Promoting the PINK1-Parkin Pathway of Mitophagy in a Murine Model of Sleep Apnea.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 24;12:628168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.628168. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717152 Free PMC article.
-
The role of reactive oxygen species in cognitive impairment associated with sleep apnea.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Nov;20(5):4. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9132. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32934669 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits are mediated by NADPH oxidase activity in a murine model of sleep apnea.PLoS One. 2011;6(5):e19847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019847. Epub 2011 May 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21625437 Free PMC article.
-
Cross talk between mitochondria and NADPH oxidases.Free Radic Biol Med. 2011 Oct 1;51(7):1289-301. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.06.033. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011. PMID: 21777669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological strategies to lower crosstalk between nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase and mitochondria.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Mar;111:1478-1498. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.128. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30841463 Review.
Cited by
-
Research journey of respirasome.Protein Cell. 2020 May;11(5):318-338. doi: 10.1007/s13238-019-00681-x. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Protein Cell. 2020. PMID: 31919741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Eye Movement sleep deprivation of rat generates ROS in the hepatocytes and makes them more susceptible to oxidative stress.Sleep Sci. 2018 Jul-Aug;11(4):245-253. doi: 10.5935/1984-0063.20180039. Sleep Sci. 2018. PMID: 30746042 Free PMC article.
-
TREM-1 and pentraxin-3 plasma levels and their association with obstructive sleep apnea, obesity, and endothelial function in children.Sleep. 2013 Jun 1;36(6):923-31. doi: 10.5665/sleep.2726. Sleep. 2013. PMID: 23729936 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of oestradiol receptor alpha and beta against hypertension and brain mitochondrial dysfunction under intermittent hypoxia in female rats.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019 Jun;226(2):e13255. doi: 10.1111/apha.13255. Epub 2019 Jan 30. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2019. PMID: 30635990 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hypoxic Injury in Mood Disorder.Neural Plast. 2017;2017:6986983. doi: 10.1155/2017/6986983. Epub 2017 Jun 22. Neural Plast. 2017. PMID: 28717522 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akki A, Zhang M, Murdoch C, Brewer A, Shah AM. NADPH oxidase signaling and cardiac myocyte function. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2009;47:15–22. - PubMed
-
- Albin RL, Greenamyre JT. Alternative excitotoxic hypotheses. Neurology. 1992;42:733–738. - PubMed
-
- Aldieri E, Riganti C, Polimeni M, Gazzano E, Lussiana C, Campia I, Ghigo D. Classical inhibitors of NOX NAD(P)H oxidases are not specific. Curr Drug Metab. 2008;9:686–696. - PubMed
-
- Andreyev AY, Kushnareva YE, Starkov AA. Mitochondrial metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2005;70:200–214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

