Improved probabilistic inference as a general learning mechanism with action video games
- PMID: 20833324
- PMCID: PMC2956114
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.07.040
Improved probabilistic inference as a general learning mechanism with action video games
Abstract
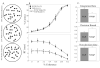
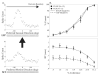
Action video game play benefits performance in an array of sensory, perceptual, and attentional tasks that go well beyond the specifics of game play [1-9]. That a training regimen may induce improvements in so many different skills is notable because the majority of studies on training-induced learning report improvements on the trained task but limited transfer to other, even closely related, tasks ([10], but see also [11-13]). Here we ask whether improved probabilistic inference may explain such broad transfer. By using a visual perceptual decision making task [14, 15], the present study shows for the first time that action video game experience does indeed improve probabilistic inference. A neural model of this task [16] establishes how changing a single parameter, namely the strength of the connections between the neural layer providing the momentary evidence and the layer integrating the evidence over time, captures improvements in action-gamers behavior. These results were established in a visual, but also in a novel auditory, task, indicating generalization across modalities. Thus, improved probabilistic inference provides a general mechanism for why action video game playing enhances performance in a wide variety of tasks. In addition, this mechanism may serve as a signature of training regimens that are likely to produce transfer of learning.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Castel AD, Pratt J, Drummond E. The effects of action video game experience on the time course of inhibition of return and the efficiency of visual search. Acta Psychologica. 2005;119:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Greenfield PM, DeWinstanley P, Kilpatrick H, Kaye D. Action video games and informal education: effects on strategies for dividing visual attention. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology. 1994;15:105–123.
-
- Bialystok E. Effect of bilingualism and computer video game experience on the Simon task. Canadian Journal of Experimental Psychology. 2006;60:68–79. - PubMed
-
- Orosy-Fildes C, Allan RW. Psychology of computer use: XII. Videogame play: Human reaction time to visual stimuli. Perceptual and Motor Skills. 1989;69:243–247.
-
- Feng J, Spence I, Pratt J. Playing an action video game reduces gender differences in spatial cognition. Psychological Science. 2007;18:850–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

