Rho-kinase directs Bazooka/Par-3 planar polarity during Drosophila axis elongation
- PMID: 20833361
- PMCID: PMC3131216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.08.011
Rho-kinase directs Bazooka/Par-3 planar polarity during Drosophila axis elongation
Abstract
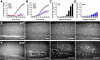
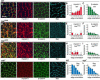
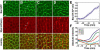
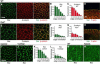
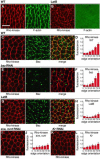
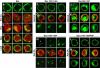
Cell rearrangements shape the Drosophila embryo via spatially regulated changes in cell shape and adhesion. We show that Bazooka/Par-3 (Baz) is required for the planar polarized distribution of myosin II and adherens junction proteins and polarized intercalary behavior is disrupted in baz mutants. The myosin II activator Rho-kinase is asymmetrically enriched at the anterior and posterior borders of intercalating cells in a pattern complementary to Baz. Loss of Rho-kinase results in expansion of the Baz domain, and activated Rho-kinase is sufficient to exclude Baz from the cortex. The planar polarized distribution of Baz requires its C-terminal domain. Rho-kinase can phosphorylate this domain and inhibit its interaction with phosphoinositide membrane lipids, suggesting a mechanism by which Rho-kinase could regulate Baz association with the cell cortex. These results demonstrate that Rho-kinase plays an instructive role in planar polarity by targeting Baz/Par-3 and myosin II to complementary cortical domains.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Amano M, Fukata Y, Kaibuchi K. Regulation and functions of Rho-associated kinase. Exp Cell Res. 2000;261:44–51. - PubMed
-
- Benton R, St Johnston D. A conserved oligomerization domain in Drosophila Bazooka/PAR-3 is important for apical localization and epithelial polarity. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1330–1334. - PubMed
-
- Bertet C, Sulak L, Lecuit T. Myosin-dependent junction remodelling controls planar cell intercalation and axis elongation. Nature. 2004;429:667–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

