Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes
- PMID: 20833577
- PMCID: PMC2992599
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drup.2010.08.003
Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes
Abstract
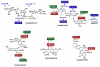
Aminoglycosides have been an essential component of the armamentarium in the treatment of life-threatening infections. Unfortunately, their efficacy has been reduced by the surge and dissemination of resistance. In some cases the levels of resistance reached the point that rendered them virtually useless. Among many known mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides, enzymatic modification is the most prevalent in the clinical setting. Aminoglycoside modifying enzymes catalyze the modification at different -OH or -NH₂ groups of the 2-deoxystreptamine nucleus or the sugar moieties and can be nucleotidyltransferases, phosphotransferases, or acetyltransferases. The number of aminoglycoside modifying enzymes identified to date as well as the genetic environments where the coding genes are located is impressive and there is virtually no bacteria that is unable to support enzymatic resistance to aminoglycosides. Aside from the development of new aminoglycosides refractory to as many as possible modifying enzymes there are currently two main strategies being pursued to overcome the action of aminoglycoside modifying enzymes. Their successful development would extend the useful life of existing antibiotics that have proven effective in the treatment of infections. These strategies consist of the development of inhibitors of the enzymatic action or of the expression of the modifying enzymes.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed AM, Nakagawa T, Arakawa E, Ramamurthy T, Shinoda S, Shimamoto T. New aminoglycoside acetyltransferase gene, aac(3)-Id, in a class 1 integron from a multiresistant strain of Vibrio fluvialis isolated from an infant aged 6 months. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;53:947–951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

